Description
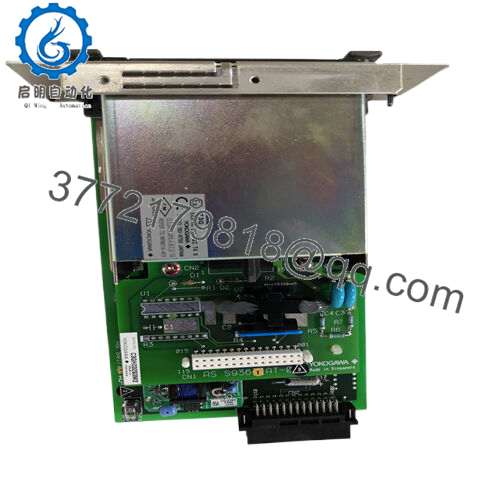
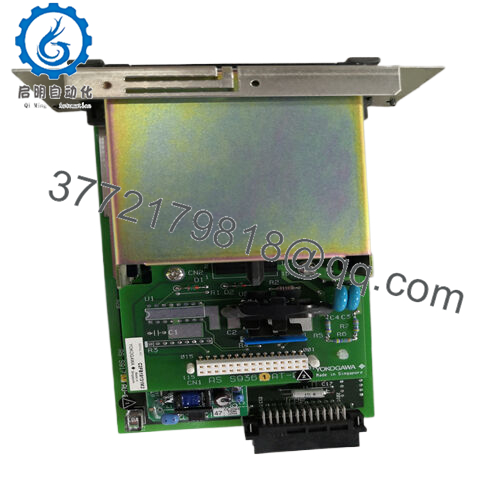
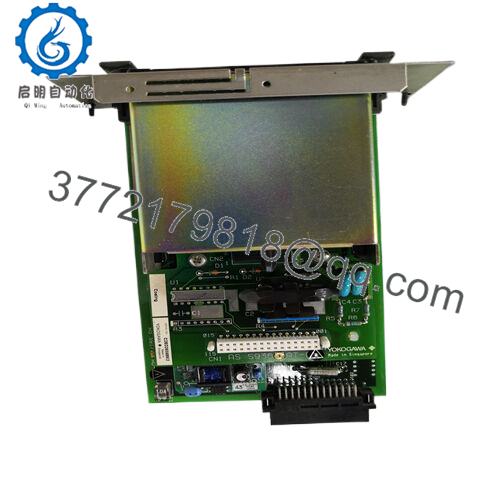
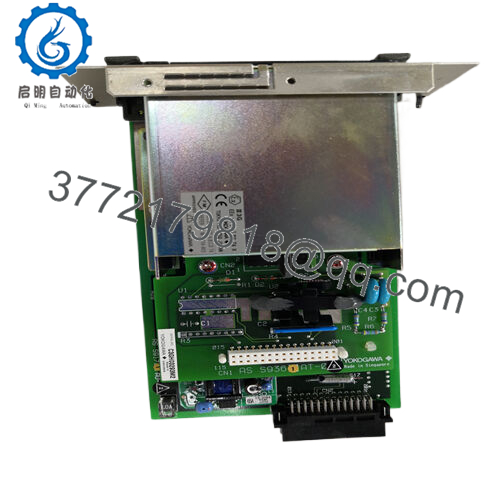
Product Model: AIP571 BUS1
Product Brand: Yokogawa
Product Series: AIP571 / RIO I/O Transceiver / Automation Controller
Product Features (based on available sources):
- Acts as a high-performance automation controller with communication interface RS-485 and support for Modbus RTU protocol
- Serves as an electrical transceiver for RIO I/O modules, linking them to FCU or other AIP571 units
- Compact and robust design with moderate operating temperature range (−10 °C to +55 °C)
- Low to moderate power consumption (AC 220 V supply listed in one source)
- AIP571 BUS1
Main Article
Below is a human-tone, detailed breakdown covering role, features, installation, specs, related models, support, and field insights. Note: some details are inferred or based on limited sources, so you should verify against the official Yokogawa datasheet.
Product Role & System Fit
In typical Yokogawa distributed systems, you’ll find AIP571 BUS1 filling the role of a transceiver / controller module that bridges remote I/O (RIO) modules and higher-level controllers or communication buses. This module is not just a passive link—it’s actively managing communication, signal conversion, and ensuring reliable data exchange.
As an electrical transceiver RIO I/O module, AIP571 BUS1 connects RIO input/output modules via fiber or electrical links to the Field Control Unit (FCU) or bus network, providing deterministic, low-latency communication. In systems where multiple RIO blocks exist, several AIP571 units may be deployed, sometimes in redundant configurations for higher availability.
In some descriptions, “BUS1” implies a variation or port designation (bus channel 1) in an architecture—i.e. AIP571 with its first bus connection type. One vendor describes AIP571 BUS1 as an “industrial automation controller” with RS-485 interface and Modbus RTU protocol use.That suggests the module can operate as a protocol converter or gateway bridging RIO networks to Modbus RTU networks.
Because the AIP571 BUS1 is used in RIO (remote I/O) schemes, its placement is typically in I/O racks, remote cabinets, or junction box sized enclosures. It must be compatible with Yokogawa’s bus backplanes and rack form factor.
In larger systems, each AIP571 BUS1 maintains communication quality, performs data retransmission, ensures integrity, and may buffer or route signals across different network segments. In critical plants, redundancy, diagnostics, and robust wiring topology are essential.
Applications & Industry Context
Where does AIP571 BUS1 see use? Here are typical scenarios drawn from system integrators and supplier descriptions:
- In distributed control systems (DCS), AIP571 BUS1 modules connect remote I/O modules to the central FCU or control processor, especially in extended or remote locations.
- In plant automation retrofits, where existing analog/digital I/O modules remain, the AIP571 BUS1 can serve as a drop-in transceiver or gateway, reducing rewiring.
- Use in industrial process control, power plants, petrochemical facilities, or utility systems where RIO modules must be gathered and transported over distance or bus segments.
- In systems that require Modbus RTU interface to external SCADA or legacy systems, the AIP571 BUS1 provides a protocol bridge over RS-485 lines.
- In applications demanding redundant communication paths, multiple AIP571 units can back one another up, preserving data flow in case one module fails.
Because the module handles critical bus and I/O link functions, its reliability, error-handling, and diagnostic features are more important than raw performance. Many plants keep spares and build the module into preventive maintenance plans.
Technical Features & Benefits
Here’s a deeper look at what AIP571 BUS1 offers in terms of design, functionality, strengths, and limitations.
Communication & Protocol Support
One source lists RS-485 as the communication interface with Modbus RTU as protocol.That means the module can serve in serial link networks, possibly interfacing legacy bus segments or SCADA front-ends.
Its fundamental role as a RIO I/O transceiver module allows it to connect remote input/output blocks to FCU or to other AIP571 modules via optical fiber or copper links. The term “electrical transceiver” implies it can drive and receive differential signals over bus cables.
Because of these roles, it must support error detection, retransmission, and buffer management to maintain data integrity under industrial noise, cable length, and multi-drop scenarios.
Power & Environmental Resiliency
One listing states AIP571 BUS1 operates from AC 220 V supply and functions between temperatures –10 °C to +55 °C. Storage range is given as –40 °C to +70 °C. Humidity tolerance is listed at 10-90 % RH, non-condensing.
These are modest environmental specs, so in harsh locations (high heat, vibration, dust, humidity) the housing, airflow, and protection must be robust.
Given the transceiver nature, internal circuits must tolerate line surges, transients, and electrical noise—designs must include isolation, surge suppression, and shielding to ensure bus stability.
Redundancy & Reliability
Because many system descriptions of the AIP571 module family mention dual-redundant ESB bus configurations, the BUS1 variant likely supports redundancy features: failover, path switching, and continuity under fault.
Transceiver modules often include diagnostic features: link status LEDs, fault registers, bus error counters, and self-test routines to detect open circuits or line errors. Even though explicit details for AIP571 BUS1 aren’t prominent in public specs, users typically expect such features in this class of module.
Compact Design & Field Serviceability
One supplier lists dimensions for AIP571 modules as about 5.1 cm × 12.7 cm × 20.3 cm, weighing ~0.3 kg. That gives a ballpark for the BUS1 variant as well. The small footprint helps pack modules in I/O racks without excessive space.
Ease of replacement is typically built in: modules like this are hot-swappable in redundant systems and connect via plug-in slot connectors to the rack backplane. Field engineers value that during maintenance windows.
Because the module may sit in relatively harsh cabinets or remote panels, it must withstand vibration, thermal cycling, and humidity over years of service.
Technical Specifications Table (Inferred / Known)
Here is a provisional spec table. Because full official specs for BUS1 variant are not widely published, you should validate or adjust these values:
| Parameter | Value / Range | Notes / Source / Caveats |
|---|---|---|
| Model | AIP571 BUS1 | |
| Brand | Yokogawa | |
| Module Type | Electrical Transceiver / Automation Controller | Based on supplier descriptions |
| Communication Interface | RS-485 (Modbus RTU) | One source lists RS-485 / Modbus RTU for BUS1 version |
| Role / Function | RIO I/O module transceiver | Connects RIO blocks to FCU or other modules |
| Power Supply | AC 220 V (some listings) | One listing indicates AC 220 V input for BUS1 variant |
| Operating Temperature | –10 °C to +55 °C | From one product description |
| Storage Temperature | –40 °C to +70 °C | From same listing |
| Humidity | 10 % – 90 % RH, non-condensing | Listed in one source |
| Weight | ~0.3 kg | Based on general AIP571 module listing |
| Dimensions | ~5.1 × 12.7 × 20.3 cm | Inferred from general AIP571 specs |
| Redundancy Support | Yes (implied) | AIP571 modules generally support redundant bus configurations |
| Link / Connectivity | Fiber or electrical bus links to RIO / FCU | General AIP571 functionality: connecting RIO I/O modules over fiber or electrical lines |
Use this as a reference sheet rather than final — get the official Yokogawa datasheet or service manual to verify every detail.
Installation & Maintenance Insights
Deploying AIP571 BUS1 in a live industrial environment requires careful planning. Here are practical tips from field experience:
Mounting & Cabinet Design
- Install in vibration-controlled racks or enclosures. Use standoffs or shock absorbers if rack motion is expected.
- Ensure adequate airflow; transceiver modules dissipate heat, especially under heavy communication loads. Avoid placing next to hot power modules.
- Shield the enclosure and cable runs from EMI (motors, drives, power inverters). Proper grounding and cable routing reduce communication noise.
Wiring & Signal Integrity
- Use twisted-pair, shielded cables for RS-485 bus segments. Terminate bus ends properly with matching resistors.
- Keep bus lengths reasonable to avoid reflections or delays. If fiber is used for long runs, ensure the AIP571 BUS1 variant supports fiber interface or use a proper media converter.
- For redundant configurations, ensure diversity in physical paths to reduce single-point failure risk.
Power & Grounding
- Provide clean, stable supply voltage. If BUS1 variant uses AC 220 V internally, ensure surge protection, isolation, and correct wiring.
- Grounding is critical: connect chassis and signal grounds per Yokogawa recommendations. Isolate signal ground from high-current or dirty power circuits.
Commissioning & Diagnostics
- After installing, verify communication links: check RS-485 connectivity, poll registers (if Modbus interface), check link LEDs and fault indicators.
- Benchmark latency and error rates. Under load, ensure the module can sustain traffic without packet loss or timeouts.
- In redundant setups, simulate module failure to ensure seamless switchover.
Maintenance & Lifecycle
- Clean dust or contamination periodically—caked dust can degrade thermal performance over time.
- Inspect connectors and cable terminations for loosening, corrosion, or damage.
- Log communication error counters and fault registers; spikes or gradual drift can signal cable degradation or module aging.
- Keep spare AIP571 BUS1 modules with matching firmware and configuration to minimize downtime.
- Protect configuration backups: store the module’s settings, register mapping, firmware ID, and revision for quick recovery.
Because modules like AIP571 BUS1 are often “invisible until they fail,” preventive maintenance combined with redundancy is the best way to maintain continuous operation.
Related Models
Here are some known Yokogawa AIP / transceiver / RIO I/O modules you may find in related systems:
- AIP571 (base version) – standard transceiver/IO module (electrical / fiber)
- AIP571 Style S1 – a variant noted in suppliers, possibly differing in interface type or ruggedness
- AIP171 – another transceiver / communication module in Yokogawa’s RIO family
- RB401 – a RIO bus module often mentioned alongside AIP571 in system catalogs
- RIO I/O blocks – the I/O modules (digital, analog) that connect downstream of AIP571 units
These modules typically share backplane, bus protocols or rack architectures, making them interoperable in many Yokogawa DCS or remote I/O configurations.





 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626


