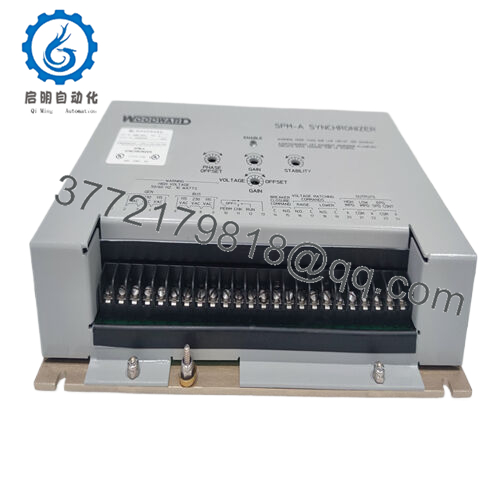
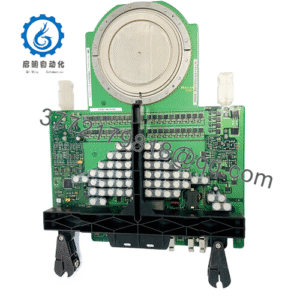
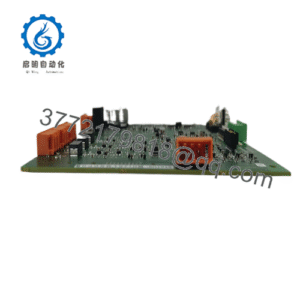
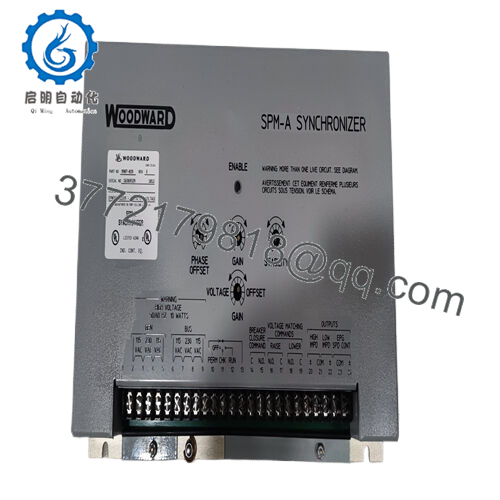
Description
In power generation and industrial automation, where generators must close onto the grid or parallel with peers without inducing surges, oscillations, or equipment damage, engineers routinely battle synchronization mismatches that stem from outdated or rigid controls. The Woodward 9907-029 confronts this as a precision-engineered SPM-A synchronizer, delivering automatic frequency, phase, and voltage matching to facilitate safe breaker closure in electric load-sharing systems. Visualize a co-generation plant ramping up during peak demand or a standby genset array engaging amid utility fluctuations—here, even brief phase drifts can cascade into torque shocks, protective trips, or grid instability. This module is indispensable in those high-reliability junctures, where robust I/O signal conditioning withstands voltage harmonics and transient spikes inherent to process control in turbine-driven setups. It champions system stability by biasing speed references dynamically, often obviating manual interventions that extend commissioning timelines or heighten operator exposure.
The Woodward 9907-029 particularly aids in retrofitting analog-era governors, where modular integration into existing panels curtails wiring revisions and downtime. Its voltage-matching prowess—tuning to within 1%—ensures seamless tie-ins across diverse alternator ratings, countering the signal unreliability that hampers legacy units in electrically noisy environments. At bottom, it aligns with users’ imperatives for dead-bus sensing and slip-frequency closure, dialing down the calibration fiddles in field trials. For turbine specialists or utility integrators eyeing resilient parallels in hybrid grids, the Woodward 9907-029 furnishes a high-reliability linchpin that transmutes synchronization pitfalls into predictable precision, bolstering industrial automation where every cycle hinges on harmonic accord.
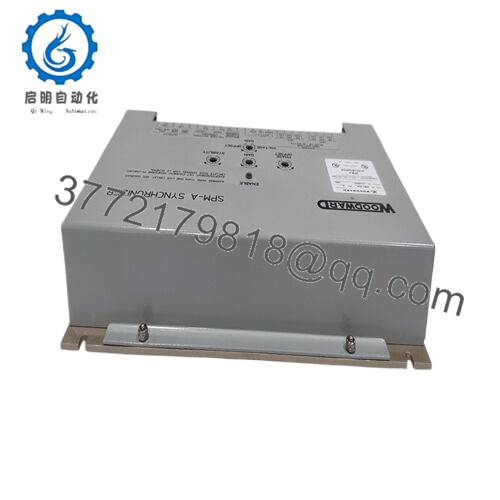
The Woodward 9907-029 integrates as the synchronization sentinel in the SPM-A lineup, perched in the load-sharing stratum of the automation stack to monitor bus and generator potentials via PT inputs, then modulate speed trim signals to the governor for alignment. It scrutinizes frequency deltas up to 50-60 Hz and phase offsets within ±10 degrees, outputting bias voltages—high-impedance for 2301 systems or low for 2301A/EPG/2500—to nudge actuators toward match points before energizing breakers. In a multi-unit island, it pairs with peer synchronizers over shared lines, enabling closed-transition transfers without voltage collapse, all while relaying sync-permit discretes to protective relays. This locates it squarely in the I/O nexus, downstream of metering transformers but upstream of the speed control loop, with inherent dead-bus detection that inhibits closure on open segments.
Diagnostics lean practical, with front-panel pots for on-the-fly dynamics tweaks—ramping fast for nimble diesels or languid for steam turbines—and LED cues for match status or fault latches, exportable via optional serial for SCADA logging. Redundancy unfolds through duplex wiring to dual governors, sustaining operation if one channel glitches, and its AC-powered design (115/230 Vac) meshes with wye or delta buses sans transformers. Rack- or panel-mounted in control cubicles, the Woodward 9907-029 galvanically isolates outputs to quash ground noise, letting technicians scale slip rates or neutral offsets through simple resistor swaps rather than deep reprogramming. This pliancy endears it to varied process control fabrics—from prime movers to peaking plants—where it dovetails with legacy architectures, trimming retrofit latency while upholding grid-compliant transients.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Number | 9907-029 |
| Brand | Woodward |
| Type | SPM-A Synchronizer |
| Input Voltage | 115-230 Vac |
| Operating Temp Range | -40°C to +70°C |
| Mounting Style | Panel/Rack Mount |
| Dimensions | 5.2 x 7.8 x 3.5 in |
| Weight | 1.1 kg |
| Interface/Bus | Analog Outputs |
| Compliance | CE, UL |
| Supported Protocols | N/A (Analog) |
| Typical Power Draw | 5 VA |
Adopting the Woodward 9907-029 embeds reliability that grapples with grid idiosyncrasies, its tunable dynamics sustaining match accuracy through alternator aging or load transients to forestall nuisance opens that idle turbines needlessly—translating to amplified availability and shaved maintenance logs in uptime-strapped industrial realms.
- 9907-029
Deployment eases markedly, as its bias outputs conform to incumbent governors sans signal converters, empowering crews to validate parallels on a test bench prior to live ties and compressing integration spans from days to hours. This lightens engineering loads in OEM skids, where standardized terminals obviate custom harnesses. Upkeep veers anticipatory; the unit’s latch-free relays self-reset on resolved mismatches, with periodic pot verifications guarding against drift, folding neatly into annual governor calibrations to preempt sync fails.
Overarching, the Woodward 9907-029 nurtures long-term performance in expanding arrays, accommodating voltage excursions up to ±10% without recalibration to embrace renewables’ intermittency, which dials in fuel savings via optimized closures. This not only curbs engineering outlays on expansions but also fortifies process control against evolving codes, yielding a leaner footprint that endures in generator fleets chasing efficiency amid flux.
The Woodward 9907-029 orchestrates grid ties in co-gen facilities, where it aligns gas turbine outputs for seamless utility handoff, furnishing high-reliability I/O amid harmonic distortion in high-load process control arenas with unyielding frequency fidelity. In marine auxiliary plants, it facilitates genset paralleling under pitch-induced swings, tolerating saline vibes while securing critical system uptime via phase-locked closures.
For industrial backup arrays in refineries, the synchronizer governs diesel banks for black-start recovery, delivering robust signal handling against EMI bursts to sustain voltage stability in explosive-zoned environments.
9905-001 – Base SPM-A model without voltage matching for basic frequency/phase apps
9907-028 – High-voltage variant for 208-480 Vac bus synchronization
9905-030 – Enhanced dynamics edition for turbine-heavy load sharing
2301A-015-018 – Compatible load-sharing controller for EPG integration
9907-252 – Load module add-on for kW/kVAR distribution post-sync 9
905-029 – Compact SPM-A alternative for space-limited panels
8237-1001 – Legacy synchronizer for economical legacy upgrades
8440-1706 – Digital easYgen companion for modern AMF extensions
When staging the Woodward 9907-029, align PT secondaries to its 115/230 Vac nominals to evade attenuation drops—under 100 Vac risks weak sensing—and survey panel bays for its 5.2-inch width, preserving 2-inch vents clear to dissipate core heat in stacked racks. Torque terminals to 10 in-lbs for vibration hold, and preset dynamics pots per engine inertia via Woodward’s app notes to sideline initial oscillations. If duplexing outputs, cross-check impedance with governor specs, as mismatches amplify bias errors.
Vigilance routines spotlight semiannual LED audits for persistent no-match flags, coupled with PT lead inspections for insulation cracks in humid vaults—a continuity probe nips opens early. Annual bench simulations with dummy loads tune slip thresholds, archiving offsets to forecast wear on pots. In paralleled banks, cycle sync duties quarterly to equilibrate exposure, de-energizing isolated first to skirt arcs. These pragmatic beats, distilled from plant audits, perpetuate the Woodward 9907-029‘s acuity with nominal effort.





 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626