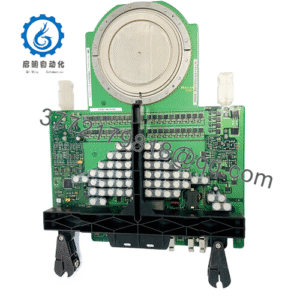
Description
In the unforgiving landscape of industrial automation, where turbine failures from uncontrolled acceleration can unleash forces capable of shredding rotors or igniting fuel lines, the margin between routine operation and disaster often hinges on detection speed and fault tolerance. Picture a gas-fired cogeneration plant grappling with erratic loads that spike RPMs beyond safe thresholds, or a hydro facility where sudden water surges overwhelm legacy relays, compromising I/O signal paths and inviting regulatory violations under API 670 or IEC 61508. These aren’t hypothetical; they’re the pulse-quickening realities in process control setups, where high reliability demands more than reactive safeguards—it requires proactive, redundant architectures that preempt overspeed without paralyzing productivity. Yet, many systems still lean on single-threaded monitors prone to drift or noise, forcing engineers into frequent calibrations or overbuilt redundancies that balloon costs and complexity.
- 8237-1600
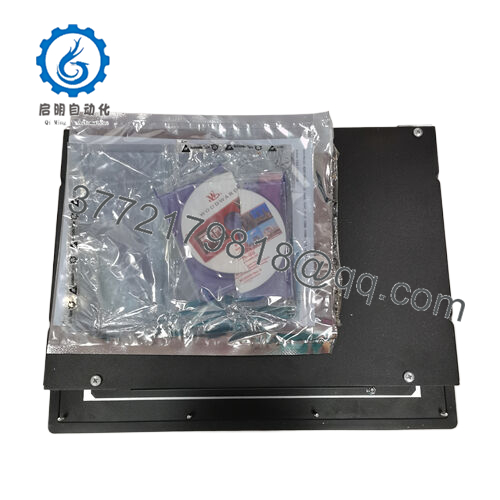
Enter the Woodward 8237-1600, a configurable overspeed protection module from the ProTech-GII lineup, purpose-built to intercept those threats with surgical precision. In high-volume deployments like offshore compression stations or utility peaking units, it emerges as indispensable during capacity expansions, where surging throughputs strain existing ESD chains; without it, teams patch with auxiliary voting logic or manual scans that erode system stability. The Woodward 8237-1600 counters by vigilantly tracking rotor speed via magnetic pickups and acceleration sensors, issuing shutdowns in under 100 ms through voted relay outputs, all while its triple modular redundancy (TMR) keeps one channel hot-swappable. This isn’t mere monitoring—it’s a conformal-coated bulwark against sulfur-laced air or vibration, ensuring I/O signal purity in class 3C2 environments.
For procurement pros sizing up options, the Woodward 8237-1600 clarifies choices with its Modbus-native integration that dovetails into DCS overlays, trimming commissioning hours and aligning with SIL 3 mandates. In turbine-heavy sectors, its automated test routines slash proof-testing overhead, turning compliance from a chore into a checkbox. Whether fortifying a steam drive in pulp mills or scaling hydro arrays, this module reframes acceleration risks into engineered certainties, delivering the modular integration and high reliability that underpin uninterrupted process control without the specter of unplanned halts.
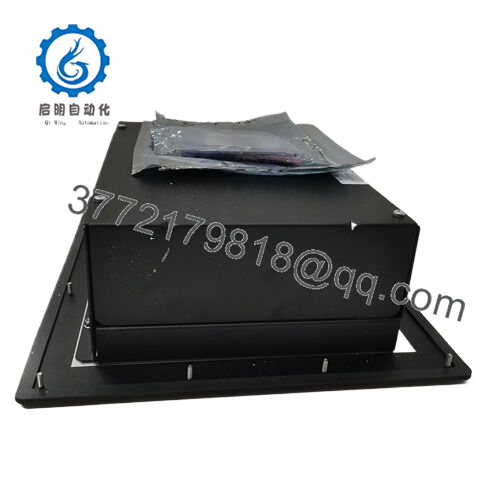
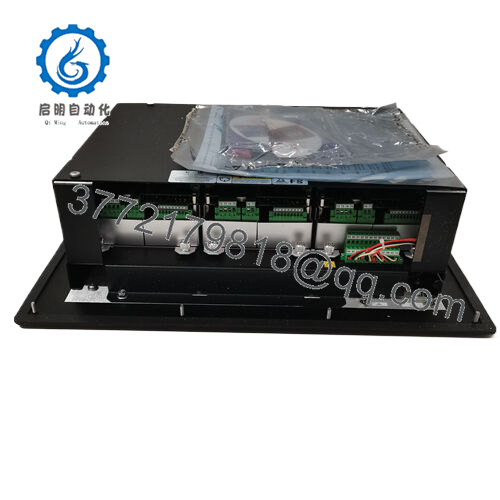
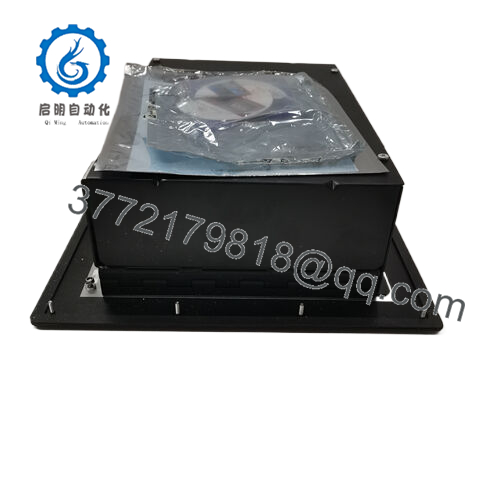
Nestled at the vigilant core of your turbine’s safety envelope, the Woodward 8237-1600 deploys as a TMR-configured sentinel in ProTech-GII enclosures, where its three synchronized modules cross-verify speed inputs from active/passive MPUs or proximity probes before propagating decisions. It panels into control kiosks alongside governor stacks or SCADA nodes, sipping from dual-redundant power rails—high-voltage AC pairs or mixed 24 VDC—to sidestep single-point vulnerabilities, while backplane interconnects shuttle diagnostics to host controllers. In the I/O architecture, it anchors upstream from trip valves, downstream of field transducers, where 4-20 mA readouts mirror rotor dynamics for operator dashboards, and configurable thresholds (2oo3 voting) filter noise without diluting responsiveness.
What elevates its fit to consultative levels is the seamless handoff: embedded logic runs periodic self-tests via internal signal generators, logging first-out faults with timestamps for forensic dives, so anomalies like probe disconnects surface before they cascade. Modbus RTU over RS-485 links it fluidly to legacy 2301 systems or Ethernet upgrades, enabling remote setpoint tweaks without halting the shaft. Envision it in a gas turbine’s startup sequence—buffering acceleration pulses to evade resonance, then fanning redundant relays to fuel shutoffs if limits breach—all while conformal coatings shrug off coastal brine. This positioning amplifies stack resilience; daisy-chain multiples for multi-spool arrays, or hybridize with analog guards for phased migrations, where galvanic isolation quells EMI from adjacent exciters. The Woodward 8237-1600 thus weaves into your automation fabric as a low-latency guardian, diagnostics that illuminate rather than interrupt, and modularity that scales with demand sans exhaustive rewires.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Number | 8237-1600 |
| Brand | Woodward |
| Type | Overspeed Protection Module |
| Input Voltage | 115/220 VAC or 24 VDC (redundant) |
| Operating Temp Range | -20°C to +60°C |
| Mounting Style | Panel Mount |
| Dimensions | 330 x 445 x 159 mm |
| Weight | <10 kg |
| Interface/Bus | Backplane, RS-485 |
| Compliance | IEC 61508 SIL 3, API 670, CE, IP56 |
| Supported Protocols | Modbus RTU |
| Typical Power Draw | 10-20 VA (inrush up to 20A) |
Embracing the Woodward 8237-1600 instills a bedrock of reliability where TMR voting nips false actuations in the bud, letting turbines navigate load swings with acceleration profiles that stay within 1% of setpoint—your processes hum steadily, unmarred by the excursions that once triggered precautionary scrams and eroded availability. In EMI-saturated bays, its isolated channels preserve I/O signal crispness, ensuring shutdown commands land decisively amid arc flashes or inverter hash, all engineered to weather 95% humidity without flinching.
Upkeep evolves into efficiency’s ally, as automated logs and LED fault trees distill troubleshooting to targeted scans—spot a drifting MPU in a glance, not a teardown—lightening engineering loads and stretching proof-test cadences to match OEM intervals. Forged for the tenacity of round-the-clock duty, it pledges enduring performance via sulfur-resistant finishes that hold firm in flue-gas proximity, honing your MTTR while steadying spares forecasts. For fleets in flux, the Woodward 8237-1600‘s hot-module swaps bypass full outages, streamlining turnarounds and recertifications alike.
Zoom out, and its Modbus fluency dissolves integration silos, funneling speed trends into asset portals for vibration correlations that preempt wear. Crews lean on fewer overrides, buoyed by intuitive test prompts that build procedural muscle memory. Opting for the Woodward 8237-1600 cements a protective ethos that anticipates escalation, fusing acute detection with tactical grace to elevate your industrial automation from reactive to resolute.
In utility gas turbines, the Woodward 8237-1600 stands watch over peaking cycles, where fuel ramps and grid eddies probe limits—its sub-100 ms trips secure critical system uptime, channeling MPU data through process control environments to quench overspeeds before they spike NOx or shear couplings.
Hydro spillways embed it for Kaplan blade guards, braving deluge mists and silt; under these harsh conditions, the Woodward 8237-1600‘s IP56 seal and SIL 3 voting deliver high reliability, auto-testing acceleration thresholds amid flow surges for glitchless synchronization.
Amid oil sands extraction, it shields steam flood pumps from torque bursts, with conformal armor suiting sulfurous digs—fast data cycles from geared tachs invoke ESD in volatile process control environments, positioning the Woodward 8237-1600 as a bedrock for industrial automation in resource-ravaged outposts.
8237-1246 – Bulkhead-mount variant for compact turbine enclosures with identical TMR logic
8237-1369 – Relay-focused enclosure housing the 8237-1600 for enhanced voted output distribution
5437-1119 – ProTech-GII successor module with added vibration inputs for compressor pairings
5437-1120 – Upgraded overspeed unit featuring Ethernet/IP for modern DCS bridges
8200-1302 – Companion digital governor for integrated speed/load control alongside protection
8237-1247 – Low-voltage dedicated model for 24 VDC-dominant hydro or backup systems
9905-001 – MPU sensor kit optimized for 8237-1600’s active/passive detection channels
5501-470 – I/O expansion board to augment 8237-1600’s discrete alarm feeds in TMR stacks
Before energizing the Woodward 8237-1600 in your ProTech-GII panel, audit enclosure grounding—per API 670, bond to chassis with <1 ohm resistance to shunt transients, and confirm MPU gap at 0.5-1.5 mm via feeler gauge to avert signal dropouts. Scrutinize power feeds for sag under inrush; a 20A breaker on 220 VAC legs prevents nuisance opens, while ambient scans ensure <60°C hotspots around vents. Firmware parity is non-negotiable—harvest the latest from Woodward’s PCT tool, validating hashes pre-load to quash glitches.
In the field, quarterly ritual: poll Modbus registers for variance logs exceeding 0.5 Hz, syncing with LED health cues for channel sync. Biannually, cue the internal test generator through the HMI—clock trip latency below 100 ms under simulated 110% overspeed—and reseat backplane connectors to 0.5 Nm, eyeing for oxidation in humid climes. For sulfur-exposed installs, annual conformal inspections via borescope catch breaches early, paired with event archive exports for trend forensics. These touchpoints slot into turbine PM cadences, upholding the Woodward 8237-1600‘s prowess without commandeering downtime.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626