Description
Real-World Use & Application Scenarios
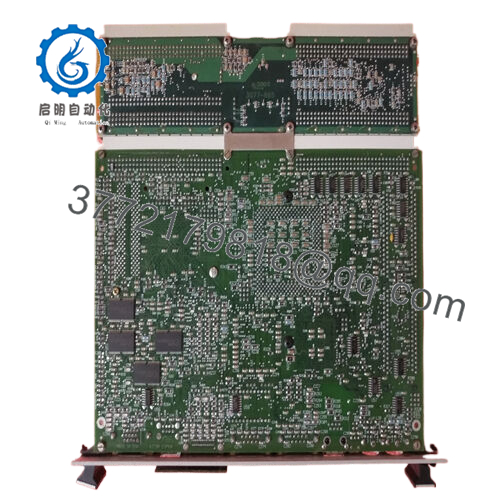
The Woodward 5466-409 is a Pentium-class CPU module widely applied within industrial control systems, particularly in power generation, oil and gas, and process automation industries. This CPU module acts as the computing core of Woodward’s MicroNet Digital Control systems, where precise, real-time processing of control logic is crucial for managing turbines, engines, and other critical machinery.
- 5466-409
Its role extends to executing complex control algorithms, managing I/O modules, and interfacing with plant automation networks to ensure smooth operation and high reliability. The module is designed to cope with the rigorous demands of modern industrial environments, including dealing with vibration, EMI, and extreme temperatures while delivering consistent performance.
Product Introduction & Positioning
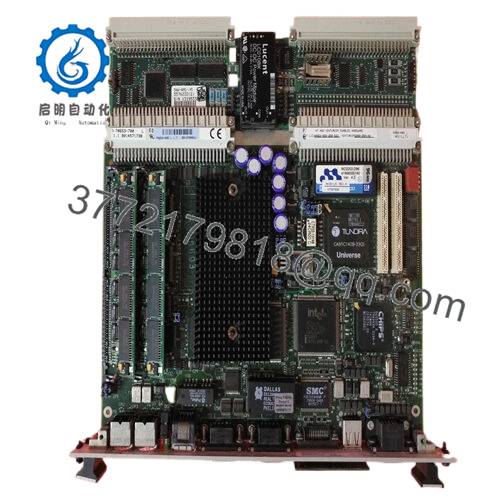
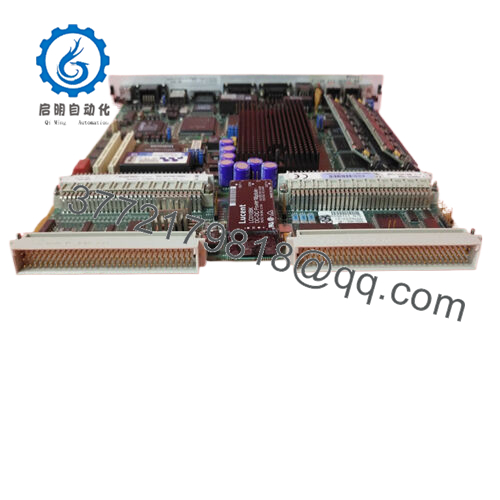
The Woodward 5466-409 is a Pentium-based processor module operating at 233 MHz, equipped with 64 MB of RAM. It integrates seamlessly into Woodward’s MicroNet Digital Control system expansion chassis and serves as the processing powerhouse for safety, speed, and load control applications.
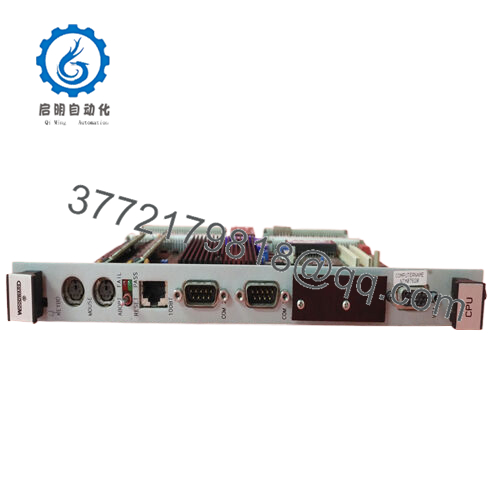
Designed for simplex systems, this CPU module includes communication ports such as Ethernet and dual RS-232 serial interfaces, enabling connectivity with other control devices and engineering workstations. It operates with a focus on reliability and compliance with industry standards like LRS, DNV, and CE (EMC).
The 5466-409 empowers engineers to develop robust, versatile control solutions with strong computation, data handling, and communication capabilities within a compact module.
Key Technical Features & Functional Benefits
The Woodward 5466-409 runs on a 233 MHz Pentium processor paired with 64 MB RAM, providing high-speed execution of control applications. Its dual RS-232 ports and single Ethernet port enable flexible, robust communication within control networks.
Operating in simplex mode, the module is designed to maintain high availability and prevent system failures in industrial control settings. It withstands operational temperatures ranging from 0 to 50°C and meets certifications from standards organizations like LRS and DNV.
The robust industrial-grade design tolerates vibration and electrical noise, crucial for installations on turbine floors and other demanding locations. Its expansion chassis capability and modular design facilitate increased system scalability and easier upgrading.
Detailed Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Model | Woodward 5466-409 |
| Brand | Woodward |
| Product Type | MicroNet Pentium CPU Module |
| Processor Speed | 233 MHz |
| Memory | 64 MB |
| Communication Ports | Dual RS-232, 1 Ethernet |
| Operating Temperature Range | 0°C to 50°C |
| Redundancy | Simplex |
| Certifications | LRS, DNV, CE (EMC) |
| Application Platform | MicroNet Digital Control Systems |
| Mounting | Expansion chassis |
Related Modules or Compatible Units
Woodward 2301D Series Load Sharing Controller – Digital engine load and speed control units related to the 5466-409 CPU.
Woodward 9907-167 Digital Governor Module – Advanced digital governor for engine speed control.
Woodward 8440-2028 I/O Expansion Modules – Supports additional analog and digital I/O expansion.
Triconex DO3625 Digital Output Module – Safety output modules used in conjunction with control CPUs.
ABB PM866K02 CPU Module – CPU module for power management systems often used alongside Woodward controls.
Installation Notes & Maintenance Best Practices
For installation, the 5466-409 must be mounted in a compatible MicroNet Digital Control expansion chassis, ensuring secure connectivity to power and communication lines. Shielded cables and proper grounding are essential for EMI resistance and signal stability.
Routine maintenance includes monitoring CPU operational parameters, running diagnostics via connected engineering workstations, and periodic firmware updates to maintain system security and functionality. Visual inspection of connectors and communications integrity checks are critical to avoid operational disruptions.




 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626


