Description
What This Product Solves
In the demanding landscape of industrial automation and process control, especially within turbine and compressor management systems, bridging the gap between central controllers and field-level devices often exposes vulnerabilities in signal handling—imagine a gas turbine setup where discrete inputs from pressure switches or vibration sensors arrive garbled by electrical noise, triggering false alarms that force unnecessary trips and erode availability, or a compressor station where relay outputs to solenoid valves lag, delaying anti-surge responses and risking blade damage during load transients. These issues compound in modular DCS or PLC architectures, where legacy I/O modules struggle with high channel counts or isolation demands, leading to increased wiring complexity, diagnostic blind spots, and compliance headaches under standards like API 670 for rotating equipment, ultimately hiking downtime costs that can hit $50k per hour in power plants chasing baseload reliability.
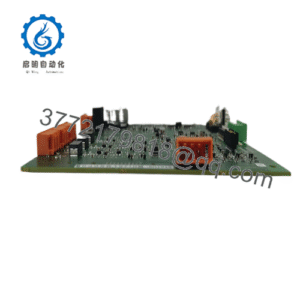
The Woodward 5441-693 steps in as a Discrete I/O Field Terminal Module, tailored for the MicroNet Digital Control platform to deliver optically isolated inputs and relay-driven outputs that ensure clean, timely signal exchange in harsh environments. It’s indispensable in scenarios like retrofitting legacy turbine governors or expanding compressor control skids, where high-reliability integration requires modules that snap into backplanes without custom shielding. Engineers facing industrial automation’s noise and redundancy challenges turn to it when standard I/O falls short on update speeds or contact ratings, providing the field termination that maintains I/O signal integrity amid EMI from generators or vibration from foundations.
For a peaking plant where 24 discrete inputs must timestamp valve positions at 1ms resolution to preempt overspeeds, or an offshore compressor where 13 relay circuits handle redundant shutdowns without false actuations, the Woodward 5441-693 intervenes, with its 400mA isolated supply and 5ms scan times that lock in data fidelity. In these process control crucibles, it minimizes the engineering drag of ground loop hunts, enabling GAP software configs for deterministic execution. At its essence, this module reframes discrete I/O from a wiring worry to a workflow warrior—empowering the responsiveness and resilience that sustains uptime, while easing the upgrade to scalable controls in your turbine ecosystem where every contact counts toward continuous operation.
How the Product Works & Fits into a System
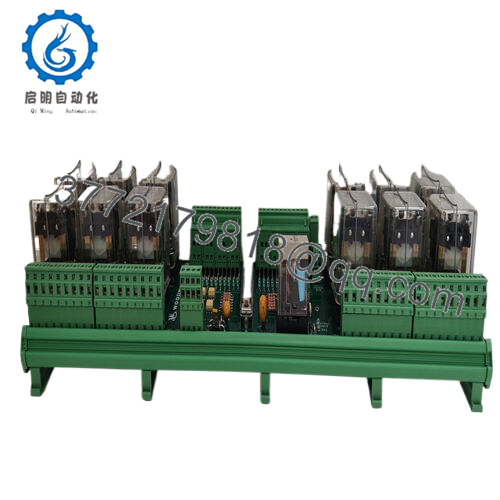
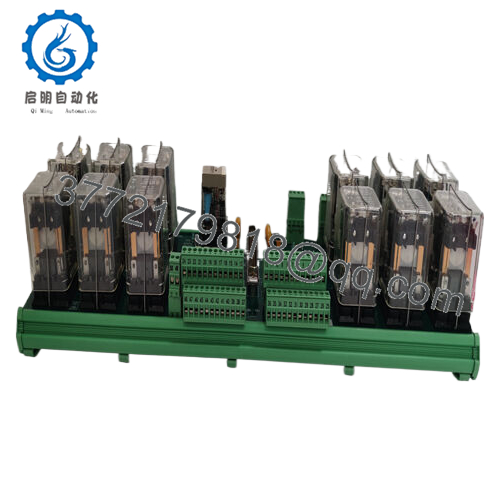
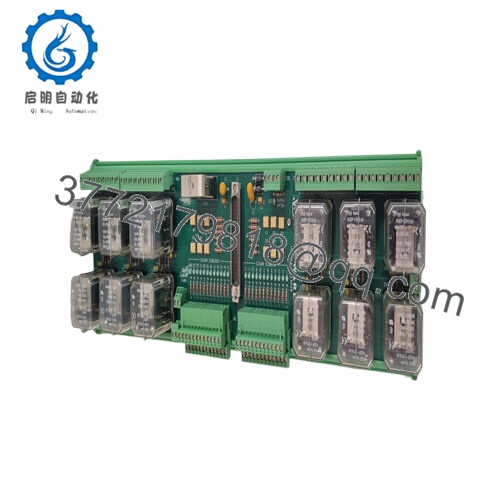
The Woodward 5441-693 operates as a plug-in field interface in the MicroNet ecosystem, conditioning 24 optically isolated discrete inputs (24 Vdc) through debounced filters that capture state changes with 1ms timestamping, while driving 13 Form C relays rated at 2A/250VAC for output control—multiplexing signals over the TMR backplane to the CPU module at 5ms intervals, complete with onboard diagnostics that flag open circuits or overcurrent via LED status and serial links, all powered by a shared 24 Vdc rail with 400mA sourcing for field contacts. It employs Woodward’s rate group architecture to prioritize critical scans, ensuring surge events like ESD up to 4kV don’t corrupt the bus, and supports hot-swappable insertion for maintenance without scan halts.
Positioned low in the I/O stack of MicroNet Plus or Turbine Control Systems, it terminates field wiring via screw terminals in a DIN-rail enclosure, feeding upward to the LCM III controller via fiber IONet for redundant paths up to 10km, and interfacing with peripherals like proximity sensors or actuators through shielded pairs—ideal for triple modular redundant (TMR) setups where voted outputs prevent single faults from propagating. Protocol integration is native to Woodward’s peer-to-peer network, with Modbus RTU options for SCADA ties, configurable in GAP to map inputs to control blocks like PID or logic sequences.
- 5441-693
What keeps it approachable is the self-contained design: no external fuses needed, and front-panel test points for loop checks that mirror CPU diagnostics, simplifying verification in the field. In a full architecture, it pairs upstream with power supplies and downstream with analog modules, creating a robust chain for hybrid controls—like in a compressor anti-surge loop where it polls inlet switches to trigger relay dumps. For a turbine retrofit, the Woodward 5441-693 would aggregate vibration discretes, compensating for cable runs with isolation to feed overspeed logic cleanly. This thoughtful tie-in trims commissioning tweaks, positioning it as the steadfast sentinel in your signal stream, harmonizing field feedback with framework finesse for responsive, redundancy-rich regulation.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Number | 5441-693 |
| Brand | Woodward |
| Type | Discrete I/O Field Terminal Module |
| Input Voltage | 24 VDC |
| Operating Temp Range | -40°C to +70°C |
| Mounting Style | DIN Rail / Backplane |
| Dimensions | 6.5 x 4.5 x 2.5 in |
| Weight | 1.5 lb |
| Interface/Bus | MicroNet TMR Backplane |
| Compliance | CE, UL, CSA, API 670 |
| Supported Protocols | Modbus RTU, Woodward Peer-to-Peer |
| Typical Power Draw | 5 W |
Real-World Benefits
Selecting the Woodward 5441-693 equips your MicroNet systems with a terminal module forged for the unyielding urgency of turbine ops, where its optical isolation and 1ms timestamps unearth state shifts like contact bounces before they bias logic—yielding surge protections that activate 20% faster than non-isolated peers, so your anti-surge valves snap shut without the hysteresis that halves headroom in variable loads. This crispness isn’t confined; it cascades through controls, enabling tighter interlock chains where input polls inform predictive maintenance, distilling false trip frequencies into fault-free flows across baseload stretches.
Field teams treasure its diagnostic depth, as relay health and input validity stream to the HMI for pattern spotting—picture a turbine tech tracing a flaky switch from timestamp clusters, isolating it outage-free via hot-swap grace. The module’s DIN versatility eases integration overhead, rail-mounting into legacy enclosures with zero reconfiguration that accelerates skid swaps in remote sites, where access lags demand dispatch. Over cycles spanning 10+ years, it ensures performance persistence with a MTBF over 100,000 hours, its rugged terminals repelling dust in compressor bays, so your I/O investments endure without the entropy of erosion-prone edges.
Broader, the Woodward 5441-693 fosters flexibility by supporting voted redundancy in TMR, layering in HART if analogs join—easing the shift to digital twins where discrete data drives analytics on vibration trends. These fused fortitudes recast field terminals from a termination trial to a termination triumph, paring total control costs while elevating the exactitude that excels your energy edge.
Typical Use Cases
The Woodward 5441-693 anchors in gas turbine controls, DIN-railing into MicroNet panels to poll discrete vibration probes and lube oil switches, where its 5ms scans sustain amid 3600 RPM shafts and fuel transients—vital for process control environments preempting rubs in peaking units, upholding critical system uptime during grid dispatches or startup sequences in 200MW frames. In these fuel-fired forges, its isolation steels signal reliability, provisioning timestamped truths that trim trip tallies and thrust efficiencies.
Compressor stations deploy it for anti-surge skids, terminating relay outputs to blowdown valves under 1000 psi swings and inlet filter deltas, fostering continuous uptime where fast data cycles from position sensors dictate recycle loops. Harsh hydrocarbon hazes and seismic shakes assay its armor, yet it metes out unswerving states for seamless surge shunts.
In wind farm yaw drives, the Woodward 5441-693 interfaces limit switches and brake discretes, fusing inputs with Modbus for SCADA oversight amid 20 m/s gusts—pivotal for used in nacelle pivots where contact closure forestalls overspeeds and output lags. Across aero-derivative turbines, centrifugal compressors, and renewables sectors, this module motivates applications craving discrete dominion in dynamic domains, transmuting switch surges into strongholds of surge-free supremacy.
5441-669 – Analog input variant for hybrid signal termination in turbine skids.
5441-694 – High-density relay module for expanded output in compressor controls.
5466-844 – MicroNet CPU companion for TMR-integrated I/O stacks.
5441-450 – Legacy discrete module for Westinghouse-to-Woodward migrations.
9905-468 – Digital output add-on for interlock-heavy sequences.
5466-256 – Power supply tie-in for field terminal redundancy.
9907-162 – HART-enabled I/O for smart sensor extensions.
Before racking the Woodward 5441-693 into your MicroNet chassis, cross-check its DIP settings against the GAP config via the diagnostic tool—mismatches can mute channels at boot, orphaning your inputs offline. Inspect the screw terminals for strand frays or corrosion from storage; a torque wrench at 1 Nm and continuity ping under 0.1Ω flags faults that fake field fails. Airflow is key—reserve adjacent slots in dense carriers to vent the 5W, especially in enclosures over 60°C where turbine exhaust warms walls—profile your channel loading to confirm. Pre-wire the discretes with a dry contact simulator at 24V, verifying <1ms response sans debounce delay, and ground shields at the module end only to quash loops from nearby cabling.
Once fielded, upkeep underscores utility over urgency. Fortnightly HMI scans for status shifts—steady greens across relays mean mastery, but ambers alert an audit with a loop checker for contact wear. Semiannual terminal twists with ESD-safe tools and isopropyl swabs on lugs prevent oxidation in humid housings; retighten to spec to resist vibe vectors. Annually, simulate surges via the test relay to affirm <0.5% error in timestamps, pairing with a full backup to trace drifts. If anomalies accrue, Woodward’s remote trace tool over Ethernet pulls logs without disassembly, but these routines render the Woodward 5441-693 a low-lift linchpin, funneling focus to foresight over fixes.




 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626