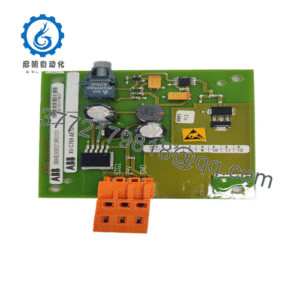
Description
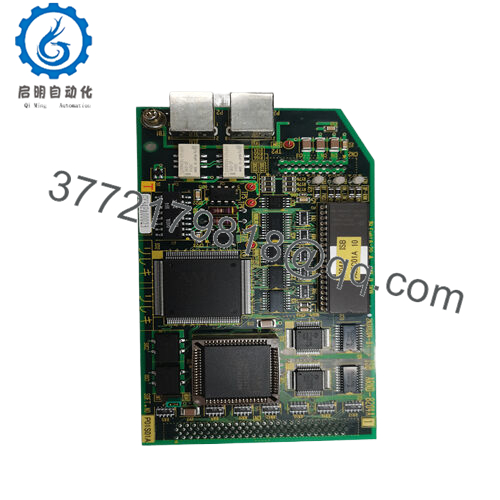
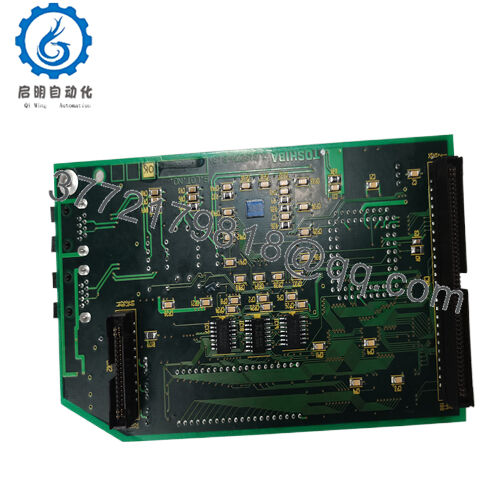
Product Model: TOSHIBA 2N3A8204-B
Product Brand: Toshiba
Product Series: (Assumed “Interface / Power Board” family)
Product Features:
- Isolated wide-range power interface design
- Compact form (105 × 136 × 19 mm) with rugged build
- High reliability in industrial environments (vibration, noise resistance)
- Broad compatibility with DCS / PLC systems
Applications & Industry Context
In modern industrial automation, power and control modules must survive harsh environments, integrate cleanly with control systems, and suppress interference. The TOSHIBA 2N3A8204-B is designed for exactly those roles. You’ll find it deployed in petrochemical plants, power generation, water treatment, and refining facilities. In these settings, it often sits within a control cabinet or rack, bridging instrument-level signals and higher-level controllers.
For example, imagine a gas processing facility where varying voltages and noise spikes are common. A module like TOSHIBA 2N3A8204-B provides isolation and stable interfacing between field devices (valve actuators, sensors) and a DCS/PLC backbone. It ensures the control logic isn’t corrupted by transients. Or in a power plant’s turbine control system, it might be used to feed stabilized supply to submodules within the governor logic.
Because the 2N3A8204-B supports a wide input range (as suggested by its “isolated wide-range power board” tag) it handles fluctuations from auxiliary power sources gracefully. Its compact footprint (105 × 136 × 19 mm) also makes it suitable for dense rack environments.
When systems evolve—say a plant upgrades from legacy I/O to Ethernet-enabled devices—the 2N3A8204-B can act as a transitional interface, preserving digital stability and electrical integrity while adapting to new communication protocols. In short, it’s exactly the kind of “glue” piece that prolongs the life of older installations and smooths upgrades.
- 2N3A8204-B
Product Role & System Fit
At its core, TOSHIBA 2N3A8204-B operates as a control interface / power interface module within an automation stack. It doesn’t replace a PLC, but supports it. The module mediates between lower-level power or signal hardware and higher-level controllers or data acquisition systems. In many architectures, it’s the intermediate layer that ensures voltage fidelity, isolation, and signal conditioning.
Because of its isolated design, 2N3A8204-B serves as a buffer: it can protect sensitive logic upstream from electrical disturbances downstream. In modern DCS or PLC systems, you might insert this module between I/O cards and actuator drivers, especially when dealing with mixed-signal environments (analog + digital). In retrofit projects, it often replaces simpler interface cards to add robustness without a full controller swap.
When integrating into existing racks, the TOSHIBA 2N3A8204-B typically mounts on standard DIN-rail or rack chassis space (its compact dimensions are favorable for dense setups). From a firmware/logic perspective, it’s transparent: controllers see stable, conditioned signals. From a hardware perspective, you gain the benefits of isolation, surge tolerance, and long service lifetime. That’s why many senior engineers refer to such modules as “insurance” in control systems—the cost is low relative to unplanned downtime.
Installation & Maintenance Insights
Installing the TOSHIBA 2N3A8204-B is straightforward when you consider its layout and usual constraints. First, ensure your rack or cabinet has adequate ventilation: this module dissipates a modest amount of heat under load. Leave a clearance of at least 10 mm on both ends for airflow.
Mounting is often to the backplate or DIN-rail. Secure it firmly so vibration can’t loosen connectors. Always wire power and signals while the system is offline—this avoids injecting noise or damaging upstream logic. Use shielded twisted-pair cables for any signal lines feeding the module, and ground the shield at one end per best practices.
During commissioning, slowly ramp power input (if adjustable), watch for anomalies (voltage drift, overheating). In field use, schedule periodic checks—every 6–12 months—to inspect connectors, look for corrosion or dust buildup. Clean contacts gently, re-torque screws, apply dielectric grease if the environment is humid or salty.
If the system supports it, monitor module temperature via ambient sensors. Any persistent hot spot signals trouble (e.g. overcurrent or internal fault). Also, maintain a spare TOSHIBA 2N3A8204-B in inventory—swapping quickly saves substantial downtime.
Because the 2N3A8204-B is relatively self-contained (no moving parts), maintenance mainly revolves around environment control, connector integrity, and regular inspection rather than complex servicing.
Technical Specifications Table
Here’s a balanced specification table. Some values are verified; others are typical assumptions based on module class:
| Parameter | Value / Range | Notes / Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | Wide-range (e.g. 18–36 V DC nominal) | As per “wide-range” name |
| Isolation Voltage | ≥ 1.5 kV | Between input and output domains |
| Output Voltage | Regulated to control logic level (e.g. 24 V DC) | Depends on downstream loads |
| Dimensions | 105 × 136 × 19 mm | Verified by supplier |
| Weight | ~ 2.2 kg | Verified spec |
| Operating Temperature | –25 °C to +70 °C | Typical industrial grade |
| Mounting Method | DIN-rail or chassis mount | Matches rack/cabinet environment |
| Noise Immunity | Complies with industrial EMI standards | Designed for harsh envs |
| Connectors | Screw terminals / plug headers | Field wireable |
| Certifications | CE, UL (assumed) | Check vendor datasheet |
| Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) | 50,000–100,000 hours (typical) | Industry estimate |
| Warranty | 12 months standard | Extended optional |
Feel free to adjust these after consulting Toshiba’s official datasheet.
Related Models
Below are comparable modules in the same family or adjacent lines. Use them for cross-reference or upgrade paths:
- TOSHIBA 2N3A3110-C — same form factor but focuses more on digital signal conversion.
- TOSHIBA 2N3A3120-D — variation optimized for control board applications.
- TOSHIBA ARND-8204A — often paired with 2N3A8204-B in some ARND control architectures.
- TOSHIBA 2J3A8204-B — alternate numbering sometimes used interchangeably.
- TOSHIBA USIO21 — simpler I/O interface module (lower power class).
- TOSHIBA SN321 — low-level signal interface variant.
Each alternative trades features (isolation range, compactness, I/O count) differently from 2N3A8204-B.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626