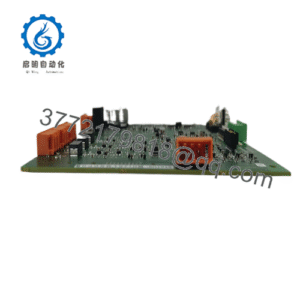
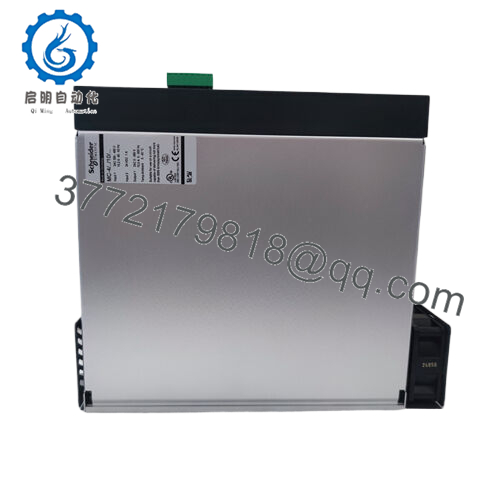
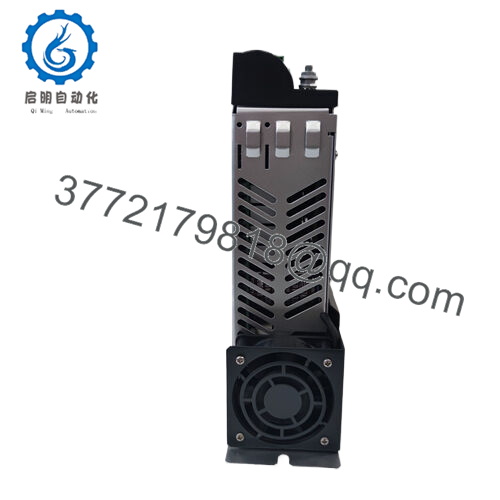
Description
Product Model: MC-41110400
- Product Brand: Schneider Electric (ELAU)
- Product Series: MC-4/11/10/400 (PACDrive MC-4 family)
- Product Features:
• 3 phase AC servo drive unit rated for 10 A output, designed for the PACDrive MC-4 motion control system.
• Input voltage: 380-480 V AC (50/60 Hz), Control voltage: 24 V DC; Output up to 0-480 V AC, 0-600 Hz.
• Discontinued by manufacturer – emphasizes importance of spare-parts strategy.

- MC-41110400
Applications & Industry Context
In a wide array of industrial automation environments — including CNC machine tools, multi-axis gantry systems, robotic work cells, and material-handling lines — precise motion control is essential. The MC-41110400 fits squarely into these contexts, as one of the higher-power modules of the PACDrive MC-4 family by ELAU (now part of Schneider Electric). When an axis demands robust drive performance — high current, variable frequency, responsive feedback control — a drive like the MC-41110400 is often used.
For instance, consider a gantry system moving a heavy sled across a large machining envelope. The servo drive must handle rapid acceleration/deceleration, sustain torque under load, and support high frequency output for rapid positioning. With the MC-41110400 (rated at 10 A / 380-480 V / up to 600 Hz) you get the capacity for a demanding axis.
Another real-world scenario: a packaging line uses multiple axes—pick-and-place, indexing, wrapping. One of those axes was initially fitted with a lower-rated drive. Over time, speed and payload increased, so the OEM upgraded to a unit like the MC-41110400. That drive’s robustness allowed the line to continue without major redesign. For maintenance teams, the ability to source a drive like this means the difference between a short downtime and expensive redesign.
Given that this drive is now discontinued (see below), teams responsible for brown-field machines increasingly view the MC-41110400 as a strategic spare. Many machines built on the PACDrive platform (MC-4 series) continue to run decades later, and maintaining compatible spares is critical to avoid catastrophic downtime.
Product Role & System Fit
The MC-41110400 isn’t just a generic VFD — it’s a dedicated servo drive module within the PACDrive MC-4 ecosystem. Its role is to control one axis (often servo motor + encoder) in a coordinated motion system. In the control architecture you’ll typically find: a PACDrive controller, a motion bus/backplane, servo drives like the MC-41110400, motors and feedback devices.
From a systems integrator’s perspective: you slot in the MC-4/11/10/400 drive into the appropriate rack or cabinet, connect 380-480 V supply to the drive’s input, connect the motor and encoder to the drive’s output, wire the 24 V DC control bus, and configure the drive parameters (current limit, frequency output, encoder input, etc.). Because the drive supports up to 0-600 Hz output and variable voltage, it fits well for high-performance axes.
Maintenance teams should note that since the MC-41110400 is discontinued, compatibility is key: the drive must match the logic of the machine (firmware version, bus interface, feedback loop parameters). Replacing with a non-compatible drive may require rewiring or re-commissioning. Hence, when sourcing a spare MC-41110400, verifying part number, variant (MC-4/11/10/400 vs MC-4/11/10/400/00), revision, and drive parameters is essential.
Technical Features & Benefits
Here are some of the standout technical features of the MC-41110400 — and the practical benefits you’ll gain in the field:
- High Input/Output Rating
The MC-4/11/10/400 drive is rated for 380-480 V AC input and produces 0-480 V AC output at up to 10 A and up to 600 Hz. This headroom means it can serve high-demand axes and operations—less risk of overload or drive thermal issues. - High Frequency Output (Up to ~600 Hz)
The output frequency capability of up to 600 Hz gives flexibility in applications needing high speed or special motors. For example, a servo motor initially rated for 3000 rpm may run at double speed if the drive supports it. This makes the system more versatile. - 24 V DC Control Supply and Compatibility
The drive takes a 24 V DC control supply (1 A) and supports the PACDrive control architecture. This ensures the drive integrates seamlessly into the machine’s control rack without additional interface modules. - Legacy Platform But Strong Support in Aftermarket
Though discontinued by the manufacturer, the drive is well documented in surplus markets and repair houses. Example: listings indicate “DISCONTINUED BY MANUFACTURER” for MC-4/11/10/400. For buyers, this means you can still find spares or refurbished units—but you should act proactively. - Robust Build for Industrial Environments
The drive is built by ELAU in Germany, designed for industrial use, likely supports rigorous environmental conditions and high duty cycles. A buyer listing indicates ambient temperature 5 °C to 45 °C (for one variant) and weight around 8-9 lbs. For your maintenance schedule, that signals you should monitor cabinet cooling and airflow. - Simplified Spare Strategy
Having a known spare (MC-41110400) means you reduce machine downtime drastically. Instead of redesigning the control system or substituting a non-compatible drive, you slot in the exact same unit. That reduces commissioning time and avoids logic changes.
In summary: choosing the MC-41110400 gives you high performance, compatibility with PACDrive systems, and the ability to execute maintenance/spare strategy efficiently — provided you verify compatibility and sourcing.
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Model | MC-41110400 (MC-4/11/10/400) |
| Brand | Schneider Electric (ELAU) |
| Series | MC-4/11/10/400 (PACDrive MC-4 family) |
| Function | Servo Drive / Servo Control Module (Motion Axis Drive) |
| Input Voltage | 380-480 V AC, 3-phase, 50/60 Hz |
| Control Supply | 24 V DC, ~1 A |
| Output Voltage | 0-480 V AC |
| Output Frequency | 0-600 Hz |
| Output Current | Approx. 10 A |
| Status | Discontinued by manufacturer |
| Typical Weight | ~8.99 lbs (≈4.08 kg) |
| Typical Application | High-performance servo motor axis drive in automation systems |
Note: Because detailed manufacturer datasheet may not be freely published, always verify revision, firmware version and connector configuration before installation.
Installation & Maintenance Insights
Drawing from field experience with modules like the MC-41110400, here are practical tips for installation, maintenance and spare strategy:
- Cabinet Power & Cooling: Ensure your control cabinet is equipped for 380-480 V supply, and the drive’s cooling is adequate. High-performance drives generate heat—make sure ventilation or fans are in good order. The listed ambient rating (5–45 °C) for one variant indicates caution with high ambient temps.
- Match Motor & Feedback System: Before replacing or installing the drive, check that your servo motor, encoder feedback, cabling and mechanical mount match what the drive expects. A mismatch in encoder resolution or wiring can cause fault trips.
- Slot & Bus Compatibility: Because the drive is part of the PACDrive MC-4 architecture, ensure slot numbering, bus interface (backplane or local wiring), and control logic match. Installing a drive with incorrect firmware or slot mapping may require logic change.
- Spare Inventory Strategy: Since the MC-41110400 is discontinued, treat any unit you acquire as a strategic spare. Label it clearly with part number, date received, test status. Consider keeping a test bench to verify spares annually.
- Commissioning Checks: After installation, check at least: drive recognition in controller, drive fault status, motor free-run test, closed-loop operation under load. Monitor for unusual heating, noise, vibration.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule periodic inspection: terminal tightening (power and control), inspect cooling fins/fans, check for corrosion/oxidation, monitor drive fault log for warnings (overtemp, overcurrent).
- Migration Planning: If your machine is expected to run for many more years, treat this as a stopgap rather than forever. Document the drive configuration, wiring harness, and logic so that when you migrate to a newer drive architecture you have the knowledge ready.





 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626