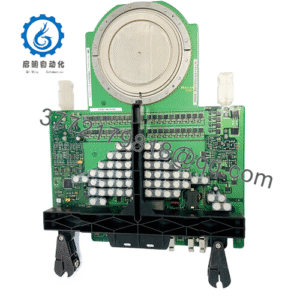
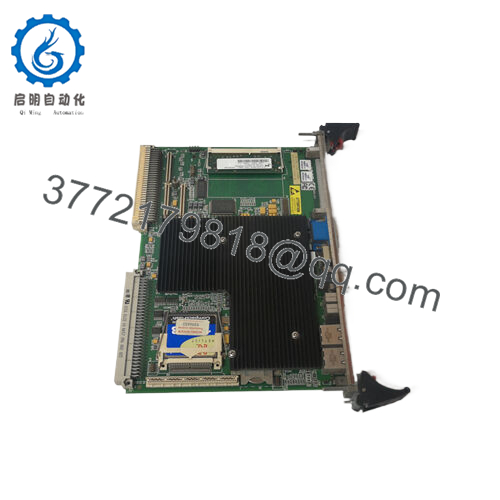
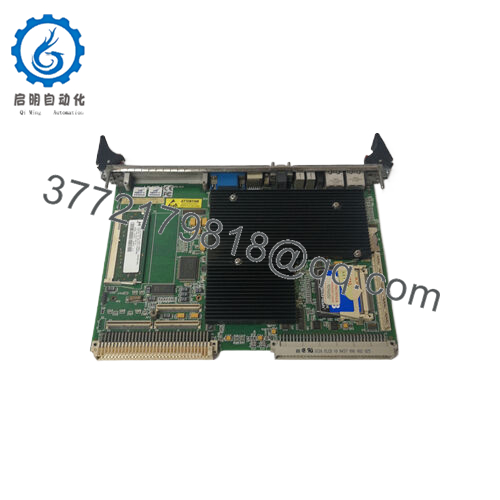
Description
- Model / Part: VMIVME-7750 (variants such as VMIVME-7750-73400, VMIVMME-7750)
- OEM Part Number: 350-027750-73400 (K / “73400” suffix variant)
- Product Nature: VME Single Board Computer (SBC)
- Core Features:
• Intel Pentium III CPU (up to 1.26 GHz)
• Supports up to 512 MB PC-133 SDRAM via SODIMM slot
• Dual Ethernet ports (10/100) & integrated VGA graphics controller
• One PMC (PCI Mezzanine Card) expansion site for modular I/O
- GE VMIVME-7750 VMIVME-7750-734001 350-027750-734001 K
Overview & Role
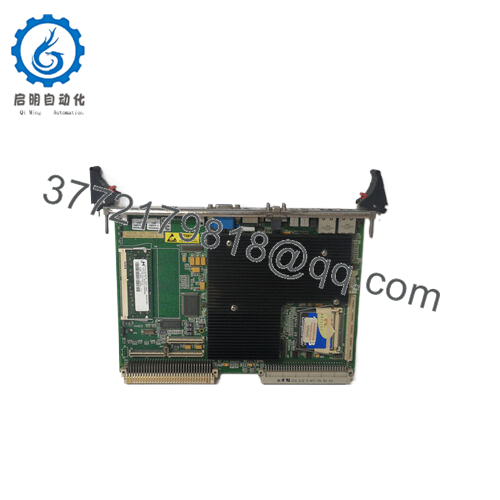
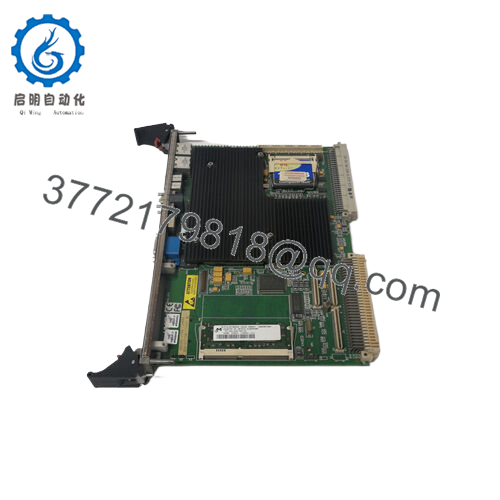
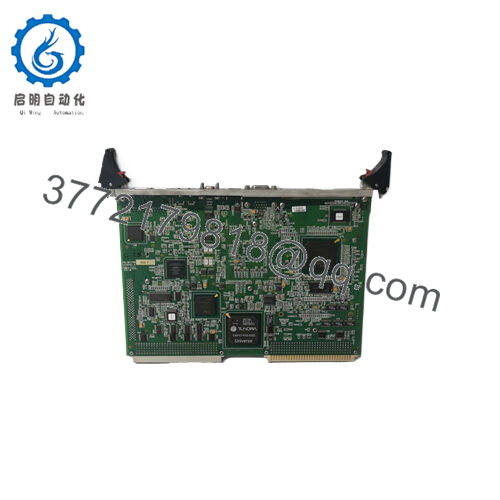
The GE VMIVME-7750 is a rugged, single-slot VMEbus single board computer (SBC) built around the Intel Pentium III architecture. It brings modern PC capabilities into VME-based embedded systems, enabling control, visualization, data acquisition, and communication tasks in industrial, power, defense, and process applications.
Variants such as VMIVMME-7750-73400 or the version with part number 350-027750-73400 (sometimes suffixed with “K”) typically indicate a particular configuration: speed grade, front panel revision, or additional features (e.g. conformal coating, temperature rating, or shipping kit). The core hardware remains the VMIVME-7750 platform, but these suffixes allow precise matching to system requirements.
This board is frequently used as a system controller or CPU node in VMEbus backplanes, running real-time OSes such as VxWorks, Linux, QNX, or custom embedded software stacks. It may also act as a peripheral CPU in more complex architectures.
Technical Features & Benefits
Processor and Memory
- Up to 1.26 GHz Pentium III with 512 KB of on-die L2 cache in high speed variants.
- Supports up to 512 MB PC-133 SDRAM via a single 144-pin SODIMM, dual-ported to the VMEbus.
Graphics & Local Display
- Integrated AGP SVGA controller with a 4 MB external synchronous DRAM cache. Supports resolutions up to 1600×1200 × 256 colors (single view mode).
- Standard BIOS and video BIOS are stored in reprogrammable flash memory.
I/O & Communication
- Dual Ethernet ports supporting 10BaseT / 100BaseTX.
- Two RS-232 serial ports (16550 UART compatible), located on front panel micro DB-9 connectors.
- USB support: onboard USB host controller with front panel connectors.
- PMC site (PCI mezzanine card) allows expansion for additional I/O or interface modules.
VMEbus Interface
- Uses a Tundra / Universe II (or Universe IIB) PCI–to–VME bridge chip, supporting VMEbus master/slave operations, window mapping, and DMA transfers.
- VMEbus features include support for BLT32/BLT64, A32/A24/A16, D32/D16, and requester/intrrupt capabilities.
- Byte-swapping support for bridging little-endian (PCI/Intel) to big-endian VME modules.
System Features
- Timers: Two 16-bit timers and two 32-bit timers, plus system timers.
- Watchdog Timer: Software-programmable watchdog; if not serviced, triggers reset or VMEbus SYSFAIL.
- Nonvolatile SRAM: 32 KB battery-backed or flash-backed SRAM to preserve state across power cycles.
- BIOS and Booting: BIOS in flash, supports booting from CompactFlash or network via remote Ethernet boot (BootWare).
- Rugged / Industrial Configuration: Typically supports standard ambient range (0–50 °C) or extended options, noncondensing humidity, VME 6U form factor.
Specification Table
| Specification | Value / Notes |
|---|---|
| Product / Variant | VMIVME-7750 (e.g. “-73400 / K” variant) |
| Processor | Intel Pentium III, up to 1.26 GHz |
| L2 Cache | 512 KB (variant dependent) |
| Memory | Up to 512 MB PC-133 SDRAM (via SODIMM) |
| Graphics | AGP SVGA with 4 MB DRAM cache |
| Ethernet | Dual 10/100 Mbps ports |
| Serial Ports | Two RS-232 (16550) |
| USB | Front panel USB host support |
| VME Interface | PCI-to-VME bridge (Universe II / IIB) |
| VME Modes | Master/slave, BLT32/BLT64, A32/A24/A16, D32/D16 |
| Expansion | One PMC slot (PCI mezzanine) |
| Timers / Watchdog | 2×16-bit, 2×32-bit timers; programmable watchdog |
| Nonvolatile Memory | 32 KB SRAM / flash backup |
| Boot Options | Boot from flash, Ethernet (BootWare), CompactFlash |
| Power Requirements | +5VDC: ~6 A typical, +12VDC, –12VDC loads (serial) |
| Operating Temperature | 0–50 °C (standard); extended options possible |
| Form Factor | 6U single-slot VMEboard, Eurocard style |
Installation & Maintenance Notes
From field experience and manual references:
- Board Insertion / Extraction: Use the board’s ejector / handle mechanism; ensure the card is fully seated to avoid bus faults.
- Cooling / Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow in the VME chassis; heavy CPU loads or high ambient may require forced cooling.
- Grounding / Shielding: Proper chassis bonding is crucial, especially for VME backplane noise suppression.
- Memory / Flash Upgrades: When replacing memory or flash components, ensure compatibility (PC133 SODIMM for SDRAM).
- Firmware / BIOS Updates: Apply firmware from trusted sources; backup existing BIOS and parameter sets before patching.
- RTC / Battery / SRAM Check: If equipped with battery-backed SRAM, verify battery health periodically to avoid data loss.
- Diagnostic Tools: Use onboard BIST (Built-In Self-Test) and hardware monitor logs post power-up for health checks.
Variants and Suffix Interpretations
Suffixes like “73400 / K / 350-027750-73400” generally identify:
- Specific speed grade or temperature-rated variant (e.g. 734 variant)
- A specific front-panel configuration or revision (K may denote a packaging / kit)
- Internal ordering / revision number used by GE / VMIC for tracking manufacturing differences
For example, a listing for VMIVME-7750-734 shows dimensions (263 × 58 × 28 mm) and a weight of ~0.43 kg.
Always verify with the hardware label or supplier datasheet to confirm the exact variant.
Use Cases & Industry Context
Because of its VME architecture and general-purpose capability, the VMIVME-7750 is widely used in:
- Industrial control systems (e.g. SCADA front-ends)
- Power plant control and monitoring
- Embedded automation systems requiring both compute and field interface
- Legacy VMEbus infrastructures needing modern CPU upgrade
- Defense, aerospace, test & measurement systems using VME as a standard
Over time, many installations replacing aging VME boards have used the VMIVME-7750 to modernize control nodes without changing the overall system topology.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626