Description
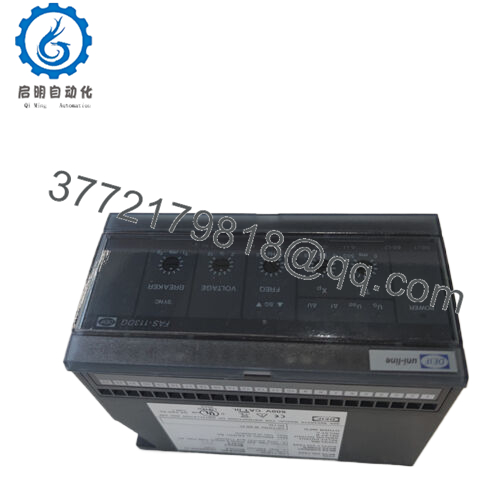
Product Model: FAS-113DG
Product Brand: DEIF
Product Family / Series: Uni-Line Synchronisers
Key Features:
- Automatic synchronisation of generator to busbar and timed circuit breaker closing, considering voltage, frequency, and phase angle limits.
- Integrated voltage regulation and breaker-time compensation for reliable synchronization under varied conditions.
- LED status and indication (voltage match, sync, active control) for visual diagnostics.
- Flexible mounting: 35 mm DIN-rail or base mounting, with spacing and airflow considerations.
- FAS-113DG
Product Role & Application Context
In power generation, one of the critical tasks is to bring a generator into synchronism with a busbar and then close the circuit breaker at the precise moment so as to avoid damaging transients, phase mismatch, or voltage/frequency shock. That’s exactly what DEIF’s FAS-113DG is designed for: to monitor generator and busbar electrical quantities (voltage, frequency, phase), compare them within defined tolerances, and issue timing pulses to the breaker when conditions are met.
Because the module includes built-in compensation for breaker closing time (i.e. the time delay of the physical breaker), it can adjust phase angle decisions so that, by the time the mechanical contacts close, the phases align. This is especially useful when there is lag or delay in breaker actuation.
You’ll often find the FAS-113DG in generator control panels, synchronization racks, or paralleling systems, paired with other DEIF components (e.g. load sharing units, protective relays). In many cases, the synchroniser is adjacent to the governor interface and breaker logic. It’s part of the “Uni-Line” set of relays for generator control.
Because it supports voltage regulation, the module also provides control pulses to bring generator voltage in step with the busbar before synchronization. That helps avoid voltage transients or “bumps” when closing.
Technical Features & Benefits
Here’s a deeper look into what the FAS-113DG offers and how it works.
Synchronisation Logic & Tolerance Control
- It continuously measures busbar voltage/frequency/phase and generator voltage/frequency/phase and computes the differences.
- It employs a slip frequency (f_set) parameter to control how slowly or aggressively the generator frequency is adjusted to match the busbar, typically in the 0.1–0.5 Hz range.
- The module uses a proportional band (Xp) setting, defining how much phase angle change is allowed relative to frequency deviation; this determines how the synchronising pulses scale with error.
- Resolver of breaker closing time (TBC) is applied: because breakers take a finite time to close (mechanical delay), the module anticipates that and injects a phase advance so that the contact point aligns at zero angle.
- Voltage tolerance (∆U_max) setting ensures the voltage difference between generator and busbar is within acceptable limits before permitting synchronization.
- The synchronising pulses are only transmitted when all criteria are met (voltage, frequency, angle) and also if the rate of change of frequency (dƒ/dt) is within acceptable bounds (i.e. not overshooting).
This multi-parameter gating ensures safer synchronization and reduces stress on equipment.
Control Outputs & Indication
- The SG ▲ and SG ▼ relay outputs drive generator speed commands (increase or decrease) during synchronization, helping to adjust generator frequency.
- The SYNC relay (or output) issues the breaker-closing pulse when synchronization conditions are satisfied.
- The module features status LEDs for mechanical/operational feedback:
- UG (generator voltage match)
- UBB or UB (busbar voltage)
- Δf (frequency difference)
- ΔU (voltage difference)
- SYNC (when sync pulse is active)
- SG ▲ and SG ▼ activation indicators
- A self-monitoring function supervises the microprocessor; a green steady light indicates normal operation; a flashing green (2–3 Hz) indicates a fault or error.
These features help operators see at a glance whether the module is satisfied all conditions or if some parameter is out of bounds.
Mounting, Protection & Physical Layout
- The FAS-113DG supports DIN rail mounting (35 mm) or base mounting via screws.
- It should be spaced from adjacent modules (≥50 mm top/bottom) to allow airflow and reduce mutual heating.
- The rail must be installed horizontally when stacking multiple units, to avoid calibration drift or mechanical stresses.
- Connectors and terminals must comply with insulation, ESD protection, and voltage ranges. A 2 A fuse may protect voltage inputs.
- For inductive loads (e.g. DC pilot motors), the built-in relays should not drive them directly; use auxiliary relays and transient suppression across coils to protect contacts.
These physical and protective guidelines ensure longevity and stable behavior.
Technical Specifications Table
The table below is drawn from DEIF’s published data sheet, installation manual, and vendor sources:
| Parameter | Value / Range | Notes / Source |
|---|---|---|
| Model | FAS-113DG | — |
| Module Type | Generator Synchroniser & Circuit Breaker Closing | |
| Synchronisation Functions | Voltage match, frequency match, phase angle gating, breaker-time compensation | |
| Input Voltage Measurement | Up to 450 VAC (typical) | |
| Supply Voltage / Logic | 24 V DC supply | |
| Mounting | 35 mm DIN rail or base mounting | |
| Weight | Approx. 0.750 kg | |
| Control Outputs | SG ▲, SG ▼ relays + SYNC relay | |
| Status Output | Open collector / status contact (Sta) | |
| Adjustable Settings | Xp (proportional band), TN (pulse duration), f_set (slip freq), ΔU_max, TBC (breaker time) | |
| LED Indication | UG, UBB, Δf, ΔU, SYNC, SG ▲/▼ status, power | |
| Isolation & Protection | Overvoltage protection, ESD protection, fuse input |
Installation & Maintenance Insights
From field experience and the installation manual, here are practical tips and cautions when deploying FAS-113DG.
Wiring & Input Protection
- Protect the voltage input circuits with a 2 A fuse in the voltage input line to prevent damage from overloads.
- When connecting breaker coil / relay loads, always use auxiliary relays and snubbers / transient suppressors across coils to avoid contact wear.
- During synchronization setup, the inhibit input (terminals 34 & 35) can be shorted to temporarily disable the SYNC relay, useful during testing or abnormal conditions.
- Tie the FS line (frequency sharing) from a load sharing control unit (e.g. LSU series) to terminals 36/35 for coordinated system synchronization.
Configuration & Commissioning
- Set TN (pulse length) initially to ~0.2 s, adjusting downward for fast-responding governors or upward for sluggish ones.
- Tune Xp (proportional band) such that the synchronizer responds but does not overshoot or hunt; start wide (±2 Hz) and reduce carefully.
- Choose slip frequency f_set: a higher value (0.5 Hz) will speed up synch, while a lower value (0.1 Hz) prioritizes accuracy and smoother closure.
- Set ΔU_max (voltage tolerance) tighter (±2%) when busbar stable, broader (±12%) under unstable grids.
- Configure TBC (breaker closure time) matching the actual breaker mechanical response (20–200 ms typical) so the phase compensation works accurately.
- After setting, test synchronization under controlled conditions—observe LED indicators, relay actuation timing, and synchronization behavior.
Maintenance & Diagnostics
- Monitor the power LED: steady green = healthy, flashing green = internal fault.
- The status output can be tied to alarms or monitoring systems to flag module errors.
- Periodically check terminal screws, wiring integrity, and inspect for corrosion or loose connections.
- If synchronization fails repeatedly, check voltage mismatch, phase wiring, or relay/contact timing rather than immediately replacing the module.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626


