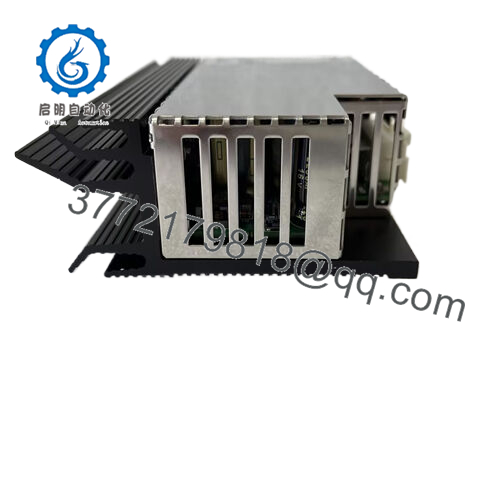
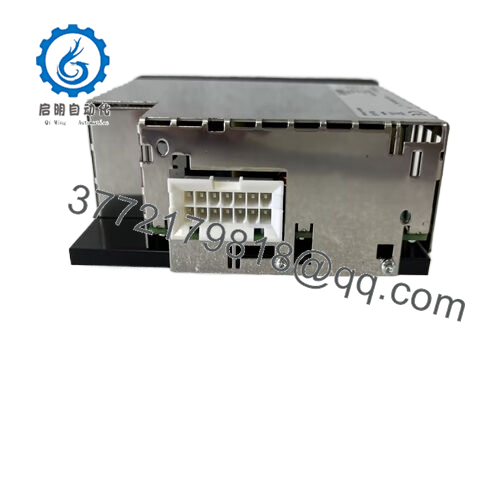
Description
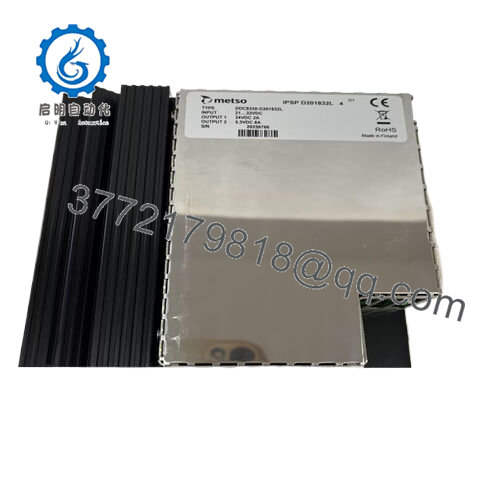
Product Model: D201832L
Product Brand: Metso (Valmet / Metso Automation)
Product Type / Series: IPSP — Integrated Power Supply & Processor Module
Key Features (from public listings):
- Functions as an IPSP (Integrated Power Supply & Processor) module, combining power supply and processing capability in a control system.
- Provides DC power supply conversion and processor execution within Metso controller architectures.
- Input / output power converter role: in a surplus listing, DDC8330-D201832L is described as a DC power converter: input voltage range 21–32 V DC, output 5.3 V and 24 V DC rails, output current ~8 A.
- Commonly paired with Metso controllers such as ACN MR D202275 and base chassis D202214 as part of the host controller stack.
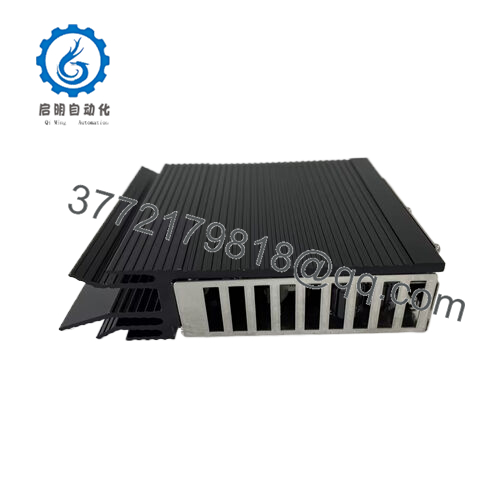
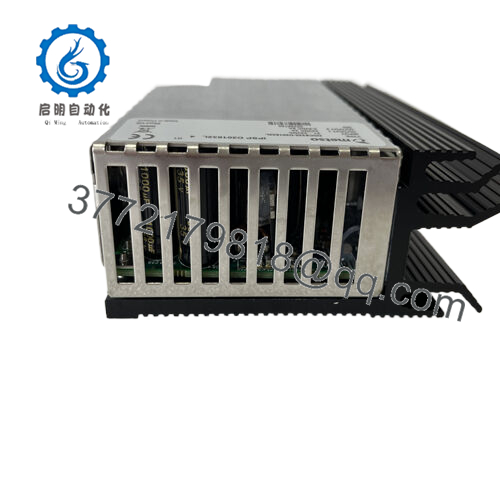
- D201832L
Role & System Integration
The Metso D201832L module plays a hybrid role in Metso’s automation control stacks. Its designation as an IPSP (Integrated Power Supply & Processor) module means it is responsible both for providing stable power rails to the system and for handling some level of processing or intracontroller logic. In many controller architectures, you will see it deployed alongside controller CPU boards, I/O bases, and network interface modules.
In a practical control rack, D201832L might sit in a slot alongside logic and I/O, drawing incoming AC or DC power, converting it to the internal DC supply rails, and supporting the module bus. It may also host control or supervisory functions (timing, diagnostics, power monitoring) as part of the integrated system.
Multiple supplier listings show D201832L paired with the ACN MR D202275 controller and D202214 base, forming a modular controller assembly. Because of this, D201832L is essential for both the “power backbone” and for enabling module-level compute in the Metso ecosystem.
One surplus listing labels it as DDC8330-D201832L, described as a DC power converter board. That listing gives insight into its internal function: transforming input DC voltage to internal rails (5.3 V, 24 V) while providing powering capability across modules.
Thus, while D201832L is not a pure logic CPU or pure I/O module, its integrated nature makes it a critical node in the controller hardware stack.
Technical Features & Benefits
Drawing from supplier data and typical module expectations, these are the major features and inferred benefits.
Power / Voltage Conversion
- In Radwell’s listing of DDC8330-D201832L, input voltage is specified as 21–32 V DC, and the output rails include 5.3 V DC and 24 V DC, with output current capability ~8 A.
- Because modern automation racks require multiple voltage levels (digital logic rails, I/O drives), D201832L likely orchestrates distribution of those voltages across modules.
- The module is listed by MRO Global as a power supply unit (“METSO D201832L POWER SUPPLY NEW IN BOX”).
- Saul Electric describes the module as providing 115/230 VAC input and output of 24 V DC at ~4 A in some listings.
These differences in listings suggest that multiple revisions exist (e.g. D201832L variant, or different build versions) and that your module’s label should be checked carefully.
Integration & Controller Support
- According to supplier catalogs, D201832L is used within Metso controller assemblies like ACN MR D202275, acting as the internal IPSP module in that configuration.
- The integrated nature reduces the number of separate power supply modules needed, improving compactness, reducing wiring complexity, and easing thermal design.
Survivability & Legacy Support
- Many listings mark DDC8330-D201832L as discontinued by manufacturer (i.e. no longer actively sold), but repairable.
- Because of that, modules are common on the surplus / industrial spare market.
- The integrated architecture means failures of this module can incapacitate both power and logic in the controller stack, so ensuring redundancy, testability, and good quality spares is vital.
Technical Specifications Table
Below is a tabular summary combining known data from supplier sources. These should be verified directly on your hardware.
| Parameter | Value / Range | Notes / Source |
|---|---|---|
| Model | D201832L (sometimes DDC8330-D201832L) | Multiple listings refer to both forms |
| Module Type | IPSP — Integrated Power Supply & Processor | Common description by suppliers |
| Input Voltage (DC) | 21 – 32 V DC (on DDC8330 listing) | Radwell listing for DDC8330-D201832L |
| Output Rails | 5.3 V DC & 24 V DC (derived) | Radwell listing describes these multiple outputs |
| Output Current (Total) | ~8 A | Radwell listing for DDC8330-D201832L |
| Input (AC variant) | 115 / 230 VAC | Saul Electric description of module input type |
| Output (Alternate variant) | 24 V DC @ ~4 A | Saul Electric listing for module output |
| Status / Availability | Discontinued / Legacy | Multiple listings note “discontinued by manufacturer” |
| Common Use | Part of Metso controller packages (ACN MR etc.) | Supplier controller stack listings |
Installation & Maintenance Insights
From field experience and modular automation practice, here are tips and caveats when working with D201832L.
Physical Installation & Placement
- Mount the module firmly in the controller rack or base chassis, with proper mechanical support and full connector engagement.
- Provide adequate cooling and spacing around the module; power / processor modules heat up and need thermal relief.
- If multiple modules are stacked, ensure that the power bus and internal wiring support current delivery without excessive voltage drop.
Power & Voltage Configuration
- Confirm whether your version is the DC input version (21–32 V DC) or an AC-input variant that accepts 115/230 VAC. Mismatching input will damage the module.
- On DC-input versions, ensure upstream DC supply is solid (voltage stability, filtering, ripple) to not stress internal regulators.
- Monitor output rails (5.3V, 24V, or whatever your module provides) under load, check for regulation, drop under full current, and noise / ripple.
Commissioning & Diagnostics
- After installation, measure all output rails with no load and then under typical load to ensure proper behavior.
- If the module includes processor features (diagnostics, control logic), verify that the logic portion communicates correctly with upstream controller modules and correctly registers status / fault signals.
- Because the module is integrated, a failure in power elements often affects logic; plan for modular removal / testability.
Spares & Lifecycle Strategy
- Since the module is discontinued, maintain at least one tested spare with matching revision.
- Label spares with revision, test data, and confirm that internal firmware (if any) is compatible.
- In the event of failure, isolate whether the fault is in the power subsystem or the processing subsystem—sometimes only part needs repair.
- Consider retrofitting or migration to newer controller architectures over time to reduce reliance on scarce modules.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626


