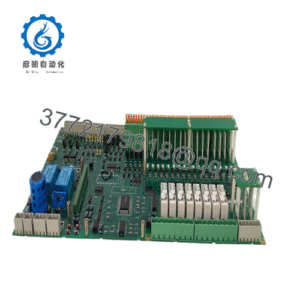
Description
Product Model: ANB11D-225/BU2A
Product Brand: Yokogawa
Product Series: ANB11D Optical ESB Bus Node Units
Key Features:
- Dual-redundant power supply node unit, optical ESB repeater for up to 5 km transmission
- Collects and relays I/O signals (analog and discrete) via optical ESB bus, supplying power to I/O modules
- Option “/BU2A” for ESB Bus connector interface (bus termination and connector unit)
- Supports environmental monitoring of cabinet via HKU interface (optional)
Main Article
Below is a technical, human-tone description of Yokogawa ANB11D-225/BU2A: system role, features, specs, installation tips, support, and application context.
Product Role & System Fit
The ANB11D-225/BU2A is an optical ESB bus node interface used in Yokogawa’s distributed I/O architectures (FIO / N-IO systems). Its role is to bridge field I/O modules (analog signals, discrete contacts) to the control side via optical transmission, while also supplying power to those I/O modules locally.
In a plant using Yokogawa’s ESB-based I/O networks, the node units are spaced across the facility. The ANB11D variant is “dual-redundant” — meaning it has redundant power and bus paths to ensure high availability. The “225” part of the suffix indicates the power supply version (220–240 V AC) and “/BU2A” designates the ESB bus connector option.
Because it acts as both a repeater and a powering node, this module is crucial for extending the ESB bus reach (optical link up to 5 km) and maintaining signal integrity across long distances or in electrically noisy environments.
In system architecture, multiple ANB11D units may be placed in remote cabinets. They collect I/O from local modules, convert and send optical bus signals toward the FCU (Field Control Unit), and possibly relay or repeat the optical bus further downstream. They can also transmit cabinet environmental data to the FCU if outfitted with the HKU option.
Because this is an optical node, it ensures isolation from ground-loop or electrical interference across long fiber spans. That is especially helpful in industrial plants with high EMI or when I/O racks are physically distant from the main control room.
Technical Features & Benefits
Optical ESB Transmission & Repeater Function
The module is capable of converting traditional I/O signals into optical signals for the ESB bus, enabling communication distances up to 5 km via multimode fiber. This extends connectivity beyond copper limitations.
It also supports dual-redundant bus connectivity: in case one bus path fails, the alternate optical path maintains communications. This greatly improves reliability in critical installations.
Dual-Redundant Power Supply
The ANB11D-225/BU2A is a “dual-redundant power supply node unit,” meaning it can be powered from two independent AC sources (e.g. 220–240 V AC) to ensure that a single power failure doesn’t bring down the node.
Power to connected I/O modules is also provided by this unit; it handles both the signal bus and the powering of the local I/O modules (analog, digital) it collects.
ESB Bus Connector / Termination Option (/BU2A)
The suffix /BU2A indicates the ESB bus connector unit used. In the ANB11D line, connector /BU2A is one of the supported interface types to align with bus topology, termination, and connector selection.
This option ensures proper physical and electrical interface to the ESB bus cables. Some variants also include terminator options (BU2B), or an HKU interface for environmental monitoring.
Environmental Monitoring via HKU
An optional interface called HKU (House Keeping Unit) allows the node to send cabinet environment data (temperature, fans, etc.) along the optical ESB bus to the FCU. This helps central monitoring of health and conditions of remote racks.
If configured, the FCU can display status, trigger alarms, and act on environmental conditions in distant cabinets.
Power & Consumption
The standard power spec for this family (ANB11S/D) includes dual AC or DC supply options. For AC, the units typically use 220–240 V AC, consuming around 230 VA / 120 W in full use.
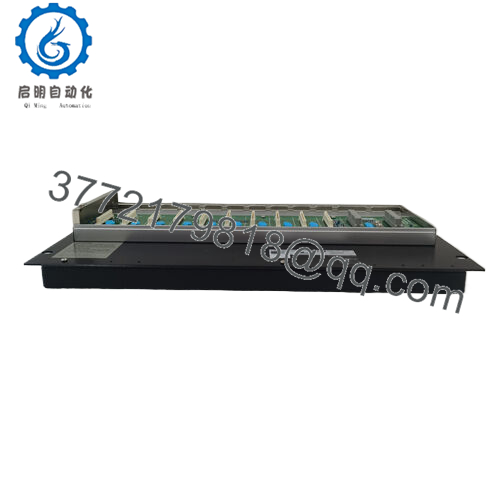
Weight is significant — the node unit, including mounted I/O modules, is roughly 10 kg.
Mounting is 19-inch rack (M5 screws) with insulation bushings as needed.
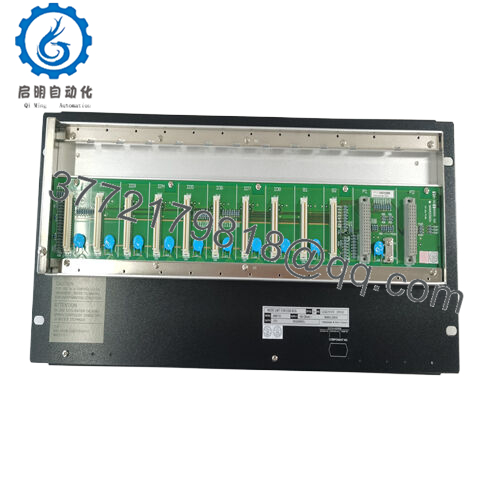
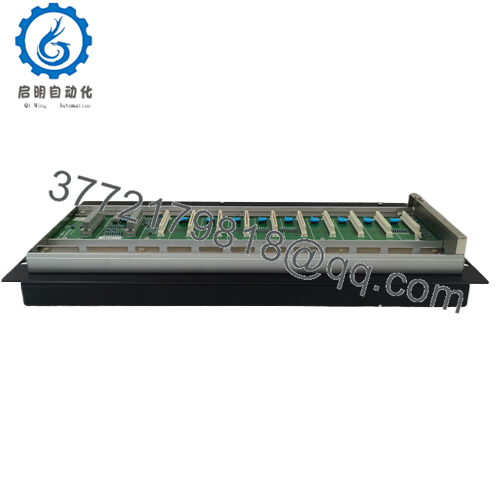
I/O Module Support
Each node supports multiple I/O modules: up to eight I/O modules (analog or discrete) can be connected in the node. This allows the node to aggregate local I/O before passing optical bus upstream.
Because the node also supplies power, it must balance signal integrity, power delivery, and redundancy among its modules.
Reliability & Legacy Support
The ANB11D family is a mature Yokogawa product line, well documented in the GS manuals (GS33J60F30) covering Optical ESB Bus Node Units. The documents specify environmental & installation constraints, bus distances, topology, module limitations, and mounting.
Because this module is often used in legacy systems or long-life plants, spare parts, replacements, and repair knowledge are generally available through Yokogawa’s service channel or automation parts suppliers.
Technical Specifications Table
| Parameter | Value / Range | Notes / Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Model | ANB11D-225/BU2A | — |
| Type | Optical ESB Bus Node Unit (Dual-Redundant) | — |
| Power Input | 220–240 V AC (dual redundant) | As per Yokogawa GS spec for AC in family |
| Power Consumption | ~230 VA, ~120 W AC | For AC supply case in GS spec for node units |
| I/O Module Capacity | Up to 8 I/O modules | Node supports mounting up to 8 I/O modules locally |
| Optical Repeater Distance | 5 km (optical link) | Model spec for 5 km repeater for optical ESB bus |
| Weight | ~10 kg (with 8 I/O modules) | From GS spec of node units |
| Mounting | 19-inch rack, M5 × 4 screws | Typical for node units in GS spec |
| Bus Connector Option | /BU2A (ESB Bus connector unit) | Suffix option for connector interface |
| Environmental Interface | Optional HKU for cabinet monitoring | Node can report environmental metrics if HKU option installed |
Please note: these numbers are drawn from the general ANB11S / ANB11D family GS documents, not from a specific published sheet of ANB11D-225/BU2A. You should confirm with the module’s actual nameplate or service manual before final engineering.
- ANBI1D-225BU2A
Installation & Maintenance Insights
Here are practical tips and caution areas when installing and maintaining ANB11D-225/BU2A nodes in real systems.
Rack & Physical Installation
- Mount the unit in a rigid 19-inch rack using the M5 screw positions. Use insulation bushings as recommended.
- Leave ventilation clearance. Because the node dissipates heat, avoid crowding other hot modules tightly around it.
- For explosion protection or harsh cabinet environments, ensure cabinet integrity per Yokogawa’s safety guidelines (metallic enclosures, filtered vents).
Power Input & Redundancy
- Use two independent, stable AC supplies (for 220–240 V) to feed the dual-redundant power circuits.
- Provide proper circuit breakers, surge protection, and wiring sized to handle the node’s full load (VA rating).
- If using DC power option (some variants of ANB10/11 nodes allow 24 V DC), maintain proper DC wiring with redundancy and protection (fuses, polarity).
Optical ESB Bus Wiring
- Use multimode fiber (e.g. 50/125 µm GI) conforming to bandwidth specs to support 5 km spans.
- Ensure pair fiber connectivity (IN/OUT), correct polarity, and low insertion loss (<7 dB typical total) as per system guidelines.
- For redundancy, layout fiber paths so that one path may be lost without full node isolation. Use dual fibers or alternate route topology.
I/O Module Integration & Powering
- Mount I/O modules (analog, digital) into the node slots, up to max 8 modules. Follow module placement and spacing rules in the GS spec.
- The node supplies power to I/O modules and field transmitters; ensure proper wiring, cable sizing, and drop compensation.
- Observe wiring for common-power and signal return paths — avoid ground loops especially since this node is optical and separates ground references.
HKU / Environmental Monitoring
- If your node is configured with HKU, connect the HKU interface (temperature sensors, fan monitors) per the module’s wiring diagram. That allows cabinet health to be monitored at the FCU.
- Periodically verify that environmental data is reporting (temperature, fan speed) and that alarms generate in FCU if conditions stray.
Commissioning & Diagnostics
- During initial power-up, verify that the optical link is active (no fiber fault) and modules detect properly.
- Check I/O modules for correct addressing and health signals.
- Monitor optical bus traffic, link errors, and latency to ensure the optical link meets system timing budgets.
- Trigger failover scenarios (cut one power leg, fiber path) to see that redundancy operates as expected.
Maintenance & Lifecycle
- Clean fiber connectors periodically; dust and debris on fiber ends degrade link quality.
- Inspect power supplies, fans, and internal wiring annually.
- Log environmental data trends (temperature, fan wear) to predict failures.
- When replacing node modules, use the same firmware version and module options to avoid compatibility issues.
For plants with long lifecycles, keeping a spare ANB11D node (with the same suffix /BU2A) in inventory is highly recommended, as full replacements may take lead time.
Related Models
Here are some sibling or variant modules in the ANB / ESB node family:
- ANB11S-225/BU2A – Single-redundant (single power supply) optical ESB node variant
- ANB11D-425/BU2A – Dual node version with 50 km optical extension capability
- ANB10D / ANB10S – Traditional ESB (non-optical) bus nodes for RIO / copper links
- ANT502 / ANT512 – Optical repeater modules for 5 km or 50 km spans, used in conjunction with ANB11 nodes
- ALR111 / ALP121 / ALE111 – Communication modules for linking ESB / subsystem networks from I/O racks
These modules share mechanical or bus interfaces and often use similar installation practices.





 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626