Description
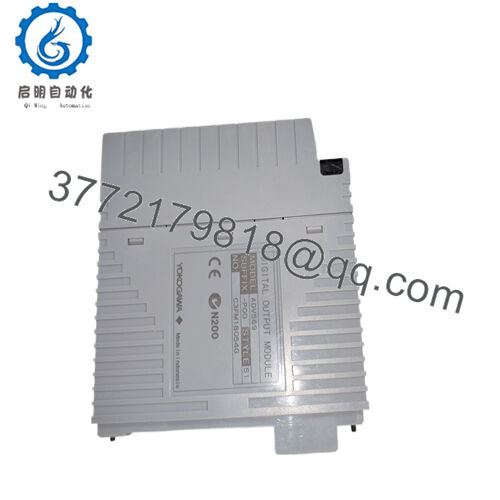
Product Model: ADV569-P00
Product Brand: Yokogawa
Product Series: ADV569 Digital Output Modules (for FIO / ST systems)
Key Features (from available sources):
- 64-channel discrete transistor output module, common minus side every 16 channels
- Support for pulse width (PW) and time-proportional (TP) output functions (–P suffix)
- Output rating: 30 V DC, 100 mA for resistive/inductive loads
- Output response time ≤ 16 ms
Technical Features & Benefits
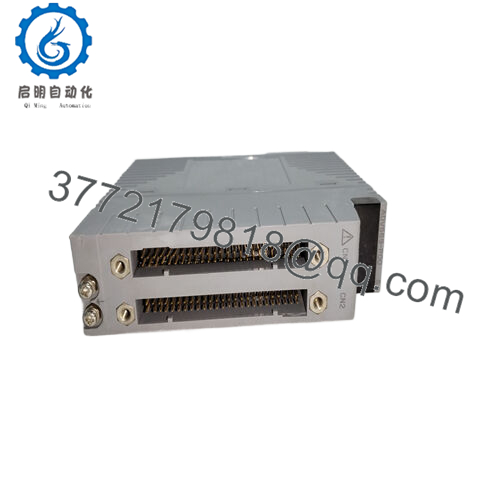
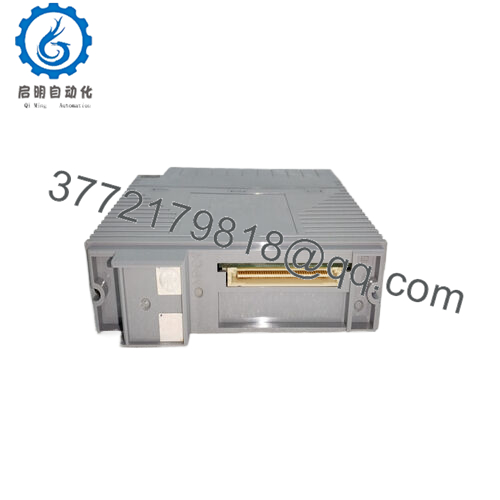
The ADV569-P00 is a high-density digital output module in Yokogawa’s FIO / ST (Station / Remote I/O) ecosystem. Its primary role is to turn control logic into physical actuation — driving field devices or indicators via discrete output channels.
One standout feature is the 64-channel output capacity — a robust module for systems requiring many control lines in a compact footprint. The outputs are discrete transistor contacts (not relay) with a common minus side arrangement every 16 channels, which is typical in Yokogawa’s digital I/O architecture.
Another key function is the support of pulse width (PW) and time-proportional (TP) outputs on suffix variants (i.e. modules with “-P” in the suffix). These modes allow more dynamic control: you can pulse outputs at specified widths or use a time-proportional method to modulate average power. The basic P00 version is the “base type.”
On electrical performance: the module supports output loading up to 30 V DC at 100 mA under resistive or inductive loads. That lets it handle modest actuator or control devices directly. The output response time is specified as 16 ms or less, a speed adequate for many process control and interlock tasks.
Because this is a discrete output card designed for Yokogawa’s I/O racks, it integrates with the station backplane, communicates with logic modules, and adheres to the FIO / ST bus protocols. It’s fully isolated per channel groups to maintain noise immunity and safety separation.
From a benefit viewpoint:
- You get lots of outputs in one module reducing module count and rack space
- Having pulse/TP modes gives flexibility in control (e.g. flashing signals, average power control)
- The discrete transistor approach offers solid-state reliability — no mechanical wear
- Integration with Yokogawa’s I/O architecture means compatibility, lower engineering overhead, and existing tools support
That said, because the module is relatively old/discontinued in many listings, field users should ensure they maintain spare modules, verify module health (e.g. drift, leakage) in preventive maintenance, and document firmware or revision numbers carefully.
Applications & Industry Context
Where is ADV569-P00 typically used? Here are realistic scenarios:
- In industrial plants (chemical, power, manufacturing), it’s used to drive valves, solenoids, indicator lights, alarms, or other ON/OFF actuators.
- In safety or interlock systems: because discrete output modules often feed emergency shutdown valves or safety relays, the fast response and isolation characteristics of ADV569 help meet safety logics.
- In process skids or modular units: a module like ADV569-P00 gives a dense output interface in limited space, reducing wiring complexity.
- In retrofits or legacy Yokogawa FIO / ST systems: many original installations used ADV569 cards, so replacements or spares of ADV569-P00 are still in demand.
- In pulse / modulation tasks: using the PW/TP features, you can achieve flashing signals, proportional control (on/off duty), or timed sequences on output lines (e.g. heater control, dosing pumps).
Because the card supports 64 channels, it’s often used in central racks that manage many outputs for a control loop cluster or safety suite rather than in very distributed remote racks. In heavy I/O environments, engineers often pair it with digital input modules (e.g. ADV151) and analog I/O hardware to build full control bloom.
Given that some listings show long lead times (22–26 weeks) for new units, many plants keep reman or refurbished ADV569-P00 modules on-hand to avoid extended downtime.
- ADV569-P00
Technical Specifications Table
Here’s a concise spec summary based on public sources (some items inferred). Always check the official Yokogawa GS / FIO / I/O manual for your version for exact numbers.
| Spec | Value / Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Model | ADV569-P00 | |
| Module Type | Digital Output Module (Discrete) | |
| Output Channels | 64 channels | |
| Output Type | Transistor contact (discrete, solid-state) | |
| Output Voltage / Current | 30 V DC, 100 mA (resistive or inductive) | |
| Response Time | ≤ 16 ms | |
| Pulse / Time-Proportional Functions | Supported on “-P” suffix variants | |
| Isolation | Common minus side every 16 channels | |
| Power / Supply | Draws up to 800 mA at 5 V DC (some listing) | |
| Weight | ~0.30 kg (some listings) | |
| Suffix / Variant Code | P = PW / TP enabled; 0 = base type | |
| Environmental / Temperature | –20 °C to +70 °C (for some suffix types) |
Again, treat this as working reference — if your plant uses a specific suffix (e.g. ADV569-P00-S1) or variant, the temperature, channel count, or power specs may shift.
Installation & Maintenance Insights
Here are practical best practices and caveats (from field experience and inferred understanding):
- Mounting & Rack Integration
The module fits into Yokogawa’s standard FIO / ST I/O racks (e.g. ESB Bus Node Units, ANB10, etc). Ensure that the bus connector is aligned correctly and that the module is fully seated. - Wiring & Interfacing
Use appropriate gauge wiring and terminal blocks when connecting outputs. Maintain consistent polarity and avoid ground loops. Because channels share a common minus side structure (per 16 channels), wiring must reflect that topology. - Pulse / TP Outputs
If using the pulse width or TP functions, ensure timing resolution, output frequency, and duty cycle settings are within supported ranges. Misconfiguring these can stress the outputs or cause coordination issues with downstream devices. - Fault Detection / Diagnostics
Watch for open-circuit conditions, short-circuit faults, and channel saturation. Regularly examine the system’s diagnostic logs for intermittent faults, which may reflect aging transistors or wiring degradation. - Replacement / Swap Strategy
Because modules like ADV569-P00 are sometimes hard to source new, keep one or more spares on hand. When replacing, ensure firmware and revision alignment, and execute a channel test (e.g. toggle outputs) to confirm proper operation before resuming full control use. - Thermal & Environment
Though the module is solid-state, high-density I/O racks can generate heat. Verify that cabinet ventilation is adequate and that ambient conditions stay within the module’s rating. Dust or humidity intrusion over long periods can degrade reliability. - Preventive Checks
Once or twice a year, check output leakage (channels that should be OFF but show small current), insulation resistance, and terminal tightness. Also, validate that the PW / TP timing behavior remains consistent (i.e. no drift).
Related Models
- ADV569-P00-S1 — variant suffix (some listings) with similar digital output function but possibly different temperature range or certification.
- ADV569 (base) — the main series name (“ADV569”) for digital output modules in Yokogawa’s FIO / ST families.
- ADV151 — digital input module complement often paired with ADV569 outputs in the same I/O rack.
- Other ADV series digital I/O modules — such as ADV859, ADV169, ADV869, etc., differing in channel count, capabilities, or application in other ST versions.
These sibling models often share mechanical form factor, rack compatibility, wiring philosophy, and I/O architecture, simplifying spare parts planning and engineering reuse.







 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626


