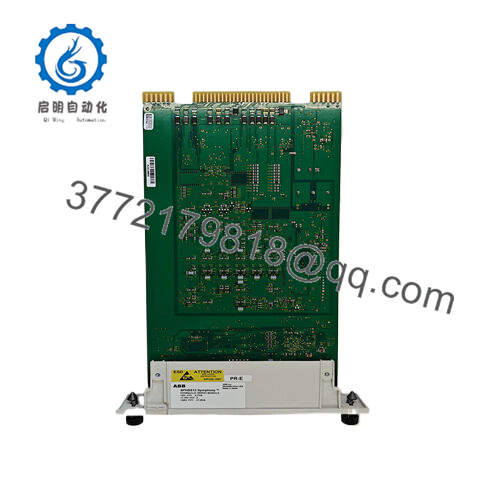
Description
In the precision-driven world of turbine and actuator control, where even minor deviations in valve positioning can unleash inefficiencies or hazards—imagine a gas turbine in a power plant where throttle valve lag during load ramps causes fuel waste and emissions spikes, or a steam boiler in a cogeneration setup where servo drift amid pressure surges leads to thermal stresses and unplanned outages—unwavering hydraulic response is the cornerstone of safe, efficient operation. These challenges loom large in industrial automation, especially in legacy Harmony Rack systems where standard servos falter under high-frequency demands, introducing signal jitter, control loop instability, or integration gaps that escalate maintenance and compliance risks in process control environments. The ABB SPHSS13 meets this head-on as a hydraulic servo module from ABB’s Symphony Plus series, rooted in the HR turbine control lineup, to deliver intelligent, redundant positioning for valves and actuators with high reliability and seamless I/O signal conditioning.
This module stands out in applications like retrofitting INFI 90-based turbine governors, where modular redundancy extends system life without full controller swaps, or in combined-cycle plants needing PI or proportional-only modes to fine-tune inlet guide vanes amid variable steam flows. In an aerospace test stand, for instance, it drives nozzle actuators under cyclic loads, leveraging LVDT feedback to hold ±0.1% repeatability and prevent overtravel that could skew test data. For offshore gas compression trains exposed to saline vibrations, the ABB SPHSS13 ensures fault-tolerant coil operation, maintaining process stability without nuisance trips. It’s particularly vital for scalable expansions in multi-stage turbines, where its onboard microprocessor offloads diagnostics from central units, aligning with goals of modular integration in EMI-saturated or high-pressure zones.

SPHSS13

SPHSS13
What elevates it in process control is its consultative edge: supporting AC/DC LVDTs for versatile feedback, it adapts to hydraulic pressures up to 350 bar without derating, while self-contained memory enables standalone tuning. In harsh enclosures or remote grids, its galvanic isolation shields against noise, and redundant coils preempt single-point failures. For engineers sustaining Symphony ecosystems, the ABB SPHSS13 bridges eras, reusing rack footprints to minimize downtime, shifting focus from reactive fixes to optimized performance in industrial automation where servo precision safeguards every cycle.
Integrating the ABB SPHSS13 into your control framework positions it as the responsive actuator driver within ABB’s HR series, where it modulates hydraulic valves via proportional outputs (4-20 mA or ±10 V) based on command signals from turbine governors like the SPTA or SPTC processors. This module mounts in Harmony Racks via backplane slots, anchoring at the field interface layer—directly commanding servo coils but relaying position feedback through LVDTs to upper logic tiers for closed-loop oversight. In a stacked architecture, it collaborates with speed detection units (e.g., SPTPS24) for governor synergy, distributing tasks across redundant pairs to evade bottlenecks in multi-valve setups.
In action, its microprocessor executes PI algorithms at 50 kHz update rates, compensating for hydraulic lags to achieve sub-millisecond settling, while dual coils enable hot-standby failover under 10 ms. Diagnostics integrate via serial links or rack bus, surfacing coil currents, position errors, or fault codes in Symphony engineering tools for predictive trending—essential in process control where remote HMI access outpaces on-site interventions. Redundancy is inherent: configure for dual LVDTs and coils to mirror operations, ensuring bumpless transfer during transients, while expandable racks host multiples for phased arrays in large turbines.
This embeddability extends to legacy hybrids: snap it into IP54 enclosures with minimal cabling, parameterize gains via front pots or software loaders, and validate loops with built-in simulators to confirm against overshoot. For rack veterans, the ABB SPHSS13 simplifies orchestration, evolving valve clusters into adaptive ensembles that scale with load profiles, enhancing industrial automation from sluggish servos to dynamic guardians.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Number | SPHSS13 |
| Brand | ABB |
| Type | Hydraulic Servo Module (Symphony Plus HR Series) |
| Input Voltage | 24 VDC |
| Operating Temp Range | -20°C to 60°C |
| Mounting Style | Harmony Rack / Backplane |
| Dimensions | 269 x 361 x 74 mm |
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
| Interface/Bus | Rack Bus, Serial |
| Compliance | CE, RoHS, IEC 61131 |
| Supported Protocols | Modbus RTU (via rack) |
| Typical Power Draw | 6 W |
Embracing the ABB SPHSS13 instills hydraulic harmony that outstrips operational volatility, its redundant coils—sustaining 350 bar without yield—clamping position errors to 0.1% in ramps where deviations forge inefficiencies or alerts, while PI modes optimize damping to curb oscillations in steam flows that plague lesser servos. This precision preserves actuator life by minimizing hydraulic cycling, easing wear on seals and pumps in high-duty turbines, all while its compact chassis fits legacy racks sans airflow disruptions.
The assimilation advantage deepens with Symphony affinity, where it repurposes INFI 90 harnesses for add-ons like redundant LVDTs, compressing tie-ins from days to diagnostics and lightening opex in turbine fleets. Upkeep refines through microprocessor logs that capture transients for early flagging, condensing probes from valve teardowns to console reviews—empowering teams to tune preemptively over patching post-fault. Engineered for endurance in steamy or particulate bays, it holds calibration across swings, deferring interventions and syncing with MTBF targets in regulated ops.
The enduring view spotlights efficiency amplifiers—modest 6 W draw trims PSU loads, while onboard intelligence defers central processing for leaner architectures that flex with valve counts. In high-reliability endeavors, the ABB SPHSS13 tempers total risks, from proportional-only fallbacks that sustain basics during faults to supervision that baselines drifts for spares, forging a servo scaffold that navigates surges in process control.
In power generation, the ABB SPHSS13 commands gas turbine fuel racks, modulating servos amid combustion roar to secure critical system uptime in process control environments where valve fidelity averts lean-burn stalls. Its high-reliability LVDT feedback processes I/O signals from throttles, ensuring load-follow precision.
Combined heat and power plants deploy it for steam bypass valves under thermal jolts in boiler halls—yielding redundant coil schemes for continuous baseload where deviations imperil district heating. In hydro governors, it drives wicket gates against water hammer in dam vaults, supporting modular wicket expansions. These roles exalt the ABB SPHSS13 as a hydraulic helm in grueling, response-rigid industrial automation, where servo savvy perpetuates poise.
SPHSS22 – Enhanced variant with triple redundancy for safety-critical turbine loops.
SPTPS24 – Speed detection companion for integrated governor architectures.
SPTA24 – Actuator driver add-on for non-hydraulic servo extensions.
INNIS11 – Legacy interface module for INFI 90-to-Harmony migrations.
SPPSS23 – Power supply mate for stable 24 VDC in rack populations.
HR-Turbine Kit – Configuration toolset for Symphony turbine setups.
SPHSS12 – Simplified proportional-only model for basic valve duties.
Symphony I/O Expander – Binary input adjunct for dense alarm integrations.
Before rack-seating the ABB SPHSS13, confirm backplane alignment—Harmony slots demand flush contacts to shun crosstalk, so probe continuity if blending series. Assay 24 VDC feeds for <2% ripple, as hums skew LVDT amps; isolate with chokes if nearby solenoids pulse. Stage firmware via ABB’s loader to match governor OS, dodging init stalls.
In the field, care distills to measured checks that respect cycles. Monthly, inspect coil LEDs for drive symmetry—balanced outputs clear paths, but imbalances cue a position log to trace hysteresis. Semiannually, inject command sweeps to verify settling under 50 ms, and cleanse terminals from oxide in humid holds. Redundant arms warrant quarterly failover tests to peg switch times below 10 ms, paired with annual rack-wide sims to affirm hydraulic loads. Drawing from ABB’s turbine guide, this routine frames the ABB SPHSS13 as a low-fuss sentinel, reaping exactitude with targeted lifts in your valve vigil.


 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626


