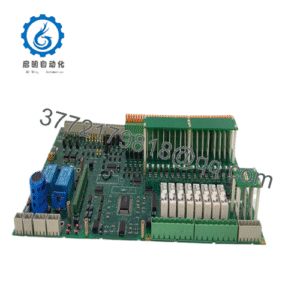
Description
What This Product Solves
In the demanding landscape of industrial automation, detecting and mitigating unbalanced currents in three-phase systems without the drag of false alarms or delayed response can feel like maintaining balance on a tightrope amid electrical storms—especially when negative sequence relays overlook harmonic distortions or phase asymmetries, causing motor overheating, reduced efficiency, and the cascading faults that disrupt process control stability and equipment longevity. Engineers safeguarding generators, motors, or transmission lines in power plants, manufacturing facilities, or renewable energy setups frequently grapple with legacy protection devices—limited to single-setting thresholds, lacking group selection, and vulnerable to CT saturation—resulting in inadequate alarming, undetected overheating, and the reactive tripping that inflates MTTR, safety risks, and operational overhead in continuous-duty environments. Envision a synchronous generator in a wind farm where unbalanced loads from grid faults go unmonitored, accelerating rotor damage and forcing unscheduled outages that curtail output amid volatile energy markets, or a large induction motor in a chemical plant where phase imbalance from feeder faults overheats windings, compromising batch integrity and inviting regulatory scrutiny under IEEE C37.106 standards.
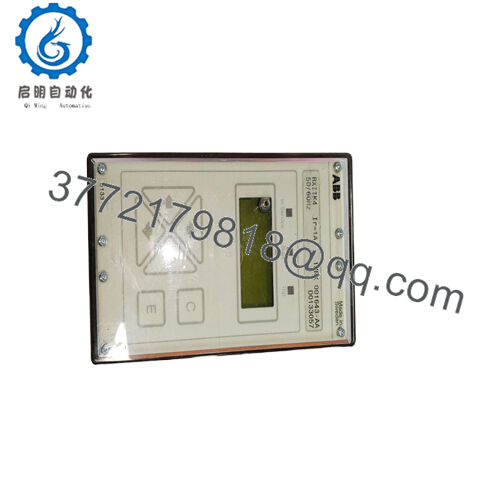
The ABB RXIIK-4 steps in as a vigilant ally, a microprocessor-based negative sequence overcurrent relay from the Combiflex series, engineered to tackle these imbalance issues head-on with its dual-setting and dual-group capabilities. It addresses the user’s core pursuit of high reliability in modular process control by providing two independent alarm/trip levels for I2t monitoring, ensuring I/O signal accuracy through transformer-isolated current inputs that buffer against transients in backplane architectures. Essential in retrofit scenarios—like upgrading legacy Combitron relays with digital supervision or scaling motor protection in distributed generation sites—this relay preempts the fault chains from unmonitored asymmetries, enabling seamless integration with SCADA for real-time trending without protocol pitfalls. For those scanning “industrial automation negative sequence relays” or “process control ABB RXIIK,” the ABB RXIIK-4 clarifies deployment viability, matching detection granularity with dynamic load demands to cut overheating incidents and enhance equipment effectiveness.
Its modular design anticipates real-world grit—dusty generator bays or humid motor enclosures—by prioritizing fault-tolerant operation with programmable outputs and HMI accessibility. No more overprovisioning thermal sensors to mask blind spots; instead, it empowers teams to focus on predictive maintenance over reactive resets, integrating smoothly into ABB Relion ecosystems. In high-stakes process control where every ampere of imbalance equates to asset attrition, the ABB RXIIK-4 redefines dependability, shifting from fault firefighting to forward-thinking fortification and fostering the current constancy that turns vulnerabilities into vigilant performance.
How the Product Works & Fits into a System
The symphony of balanced power orchestrates when relays relay not just reactions but revelations, discerning negative sequence currents without the jitter of unfiltered feeds. The ABB RXIIK-4 relays as a modular protection unit, sampling three-phase AC inputs via transformer-isolated CTs (1A/5A, up to 100 A secondary) at 50/60 Hz, computing I2 magnitude and I2t accumulation at 1-second intervals with two setting levels (alarm/trip) and two groups selectable via binary input or front HMI, then outputting via 5 programmable relays (NO/NC contacts rated 5 A/250 VAC) or serial interface for Modbus/SPA integration. Its microprocessor core applies ANSI 46 functions with harmonic restraint, looping in event recording (up to 64 events) for post-fault forensics, while the HMI enables local parameterization and disturbance recording at 20 ms resolution, and binary inputs (4) support reset/blocking in automated schemes.
In the broader I/O architecture, this relay occupies the protection tier, DIN-rail mounted in Combiflex cabinets with 1U footprint, interfacing via screw terminals for CT wiring and RS485 for network bus, syncing with ABB MicroSCANA or third-party DCS over Modbus for hybrid environments. Redundancy embeds through self-supervision and fault contacts compliant with IEC 60255 for SIL2, meshing with circuit breakers in motor or generator configs. Diagnostics integrate via PC tools like PCM600, scripting waveforms to onboard memory for sim analysis in scaled sims.
- RXIIK 4
For the deploying engineer, it’s refreshingly routinized: configure via HMI for auto-param, affix with clips, then sim network in RelaySim—commissioning condenses to hours, sidestepping the arcane wiring of electromechanical relays. Position it at the current ingress in the stack, downstream of CTs and upstream of breakers, where it transmutes imbalance into isolation—like tripping a motor before overheating escalation. The ABB RXIIK-4 doesn’t just guard; it guides, nurturing ecosystems that evolve from reactive ruptures to proactive precision, where relay rigor anticipates asymmetries, not just answers them.
Technical Highlights Summary (Table)
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Number | RXIIK-4 |
| Brand | ABB (Combiflex Series) |
| Type | Negative Sequence Overcurrent Relay |
| Input Voltage | 24-250 VDC (auxiliary via RXTUG) |
| Operating Temp Range | -25°C to +55°C |
| Mounting Style | DIN Rail / Panel |
| Dimensions | 75 mm x 150 mm x 125 mm |
| Weight | 1.5 kg |
| Interface/Bus | Screw Terminal / RS485 |
| Compliance | IEC 60255, CE, IEEE C37.90 |
| Supported Protocols | Modbus, SPA, Binary I/O |
| Typical Power Draw | 5 W |
Real-World Benefits
Choosing the ABB RXIIK-4 equips your protection framework with imbalance intelligence that quietly decimates the dangers of negative sequence currents, particularly in motor or generator applications where dual settings are the unsung hero preventing premature wear. Engineered for the grind of continuous monitoring, its I2t accumulation and harmonic restraint deliver 1% accuracy without thermal derates, ensuring performance consistency that holds trip times under 100 ms across 55°C swings—crucial for wind turbines where even fractional asymmetries cascade into bearing fatigue, but here it isolates incidents that isolate impacts, slashing maintenance costs and reclaiming runtime in reliability-driven renewables. This reliability manifests in fewer false alarms, allowing operators to push envelope on loading without compensatory derating, directly inflating capacity in distributed generation.
The relay’s modular ethos lightens the collaborative load, as DIN-rail bonding dovetails with existing cabinets via Modbus, curtailing engineering overhead in hybrid upgrades where protocol parity trumps patch quilts—teams repurpose days for sim-based settings that refine group selection. Maintenance narratives brighten too: HMI diagnostics preempt failures by trending I2 levels, stretching overhaul cadences to yearly audits—a windfall for remote crews juggling sites, where slashed site visits translate to lower TCO through fewer logistics hitches. In practice, this means fewer callouts for overheating ghosts, redirecting skilled hands to enhancements like adaptive thresholds that forecast faults.
Long-term, the ABB RXIIK-4 secures performance that outpaces expectations, from energy-efficient polling that trims kWh in idle modes to the peace of mind from self-supervision that withstands cyber threats. Engineered to anticipate asymmetries, it shifts focus from vulnerability mitigations to capability expansions, delivering the assurance that your system not only performs but persists—fostering environments where protection holds firm, innovation accelerates, and reliability becomes the quiet force multiplier in pursuit of sustainable power.
Typical Use Cases
The ABB RXIIK-4 excels in asymmetry anticipation where protection meets practicality, starting with generator safeguarding for synchronous units in wind farms. In process control environments laced with gusty grid interactions and phase shifts, it monitors I2 at dual levels for alarm/trip in unbalanced loads, where harsh wind-induced harmonics challenge connections but uphold critical system uptime—imperative for turbines generating 2 MW, minimizing rotor stress that could cascade into gearbox failures. Fast data cycles sync with Modbus for adaptive settings, ensuring seamless integration with SCADA for predictive maintenance.
In industrial motors, the ABB RXIIK-4 shields induction drives amid load lurches and feeder faults, contending with voltage imbalances from VFDs while enabling 5 programmable outputs for interlocking. Continuous uptime reigns in these bays, as its I2t accumulation prevents overheating in meshed setups, supporting SPA polling for DCS that flags asymmetries before escalation. Performance peaks in dusty factories, yet it maintains I/O fidelity, curbing curbings in high-value production.
For transmission lines, used in power grids for feeder monitoring or beyond—the ABB RXIIK-4 detects unbalanced conditions in overhead lines, enduring weather whiplash and fault inversions to trip arcs. Harsh line losses from storms test its mettle, but it delivers calibrated outputs for trending, bolstering high reliability in networks transmitting gigawatts. Across generators’ gust, motors’ might, and lines’ length—the ABB RXIIK-4 interlaces protection with prescience, fortifying flows where every ampere counts toward seamless sustainability.
Compatible or Alternative Products
RXIIK-21 – Enhanced variant with extended current ranges for higher power motors in heavy-duty applications.
RAIIK-21 – Analog companion for basic negative sequence in cost-sensitive legacy upgrades.
REF615 – Modern Relion series successor for IEC 61850 in Ethernet-enabled substations.
RXIIK-4 with HMI – Ordering code variant with local display for field-configurable in remote sites.
SIPROTEC 7SJ80 – Siemens equivalent for SIPROTEC family in cross-vendor migrations.
SEL-551 – SEL relay alternative emphasizing Modbus in North American grids.
MiCOM P120 – Schneider companion for MiCOM series in hybrid protection schemes.
PAC3200 – ABB power quality meter add-on for complementary trending in unbalanced systems.
Setup Notes & Maintenance Insights
Before DIN-railing the ABB RXIIK-4 in your motor cabinet, a compatibility check heads off config cramps: verify CT secondary (1A/5A) against the relay’s inputs via sim software, as mismatches throttle sensitivity to 5%—update firmware if below v2.0. Rail mounting demands a vibration test; fix with clips torqued to 1 Nm, ensuring 30 mm clearance for convection in 1U configs nearing 55°C. CT wiring sim is pivotal—connect three-phase with shielded cable ≤50 m, then param groups via HMI for auto-sim, as unaddressed polarity cascades detection faults. Grounding is crucial: tie cables to chassis at one end to curb induced noise in bays near VFDs.
Sustaining the ABB RXIIK-4 thrives on timely taps, not triage toils. Bi-monthly, scan LEDs for fault flickers—amber indicates CT open, sim’d with burden test <0.5 VA. Quarterly, reseat terminals in low-humidity lulls to combat pin pitting; a loupe flags oxidation, but dielectric grease preserves IP20 poise without conductance creeps. Annual diagnostic deep-dive—cycling imbalance sim via Omicron—benchmarks trip times; delays >100 ms intimate calibration creep, addressed with HMI re-param or lab recal. Firmware affinity with SCADA averts acyclical aches; propagate via RS485 during sim-only slots, attesting with event log sweep. These deliberate drills, drawn from field folios, perpetuate the relay’s 5 W mettle, channeling calibration to creative calibrations from corrective crusades.




 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626