Description
Real-World Use & Application Scenarios
Deep inside a bustling steel mill, where conveyor lines snake through clouds of dust and sparks fly from molten metal, reliable communication between drive controls and central diagnostics can prevent a single signal loss from cascading into hours of downtime. Here, units like the ABB NDBU-95C come into play, fanning out fiber optic signals to multiple drives, ensuring that speed commands and fault alerts reach every motor without delay. In the automotive assembly plants, imagine robots welding chassis frames in sync—any lag in data transmission could misalign parts, leading to scrap rates that eat into profits. This branching unit tackles that by splitting optical signals cleanly, supporting up to nine channels for seamless coordination across painting booths, stamping presses, and quality inspection stations. It’s a staple in industrial automation, particularly where ABB’s DDCS (Drive Diagnostic Communication System) networks span wide areas, demanding low-latency links to keep operations fluid.
Consider pharmaceutical production floors, sterile and regulated, where precise variable speed drives handle mixing and filling processes. Fluctuations in signal integrity might compromise batch purity, inviting regulatory headaches. The ABB NDBU-95C addresses this by enabling star topology connections that distribute diagnostic data robustly, allowing real-time monitoring of vibration levels or torque outputs to flag issues early. In renewable energy setups, like wind turbine farms, harsh offshore conditions batter equipment, yet fiber optic branching ensures control signals from onshore stations reach remote converters without corruption from electromagnetic noise. Mining operations underground rely on it too, extending communication to haulage systems and ventilation controls, where a failed link could strand workers or halt ore extraction.
What makes the ABB NDBU-95C indispensable in these control systems is its ability to handle plastic fiber optics at 10 Mbps per channel, bridging the gap between master controllers and field devices in ABB ACS and DCS800 drive families. Engineers specify it for scenarios demanding redundancy in data paths, cutting mean time to repair in environments prone to cable wear or interference. By integrating naturally with Profibus or Ethernet overlays, it supports predictive analytics that optimize energy use in HVAC retrofits or pump stations, aligning with sustainability pushes in manufacturing. Ultimately, it’s the quiet hero that turns fragmented networks into unified, responsive ecosystems, empowering teams to focus on output rather than outages.
Product Introduction & Positioning
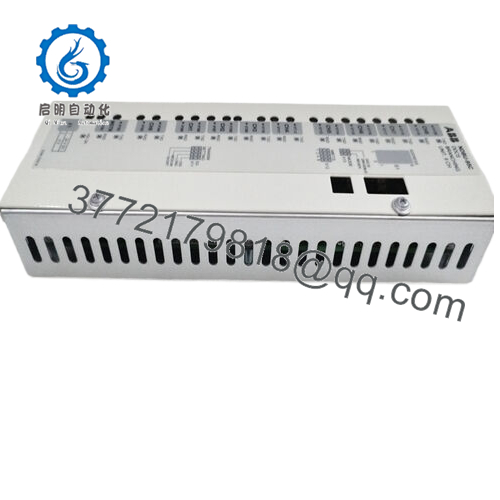
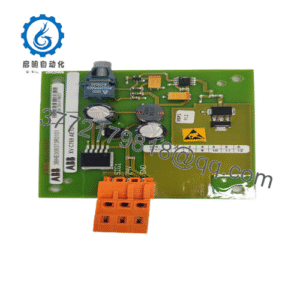
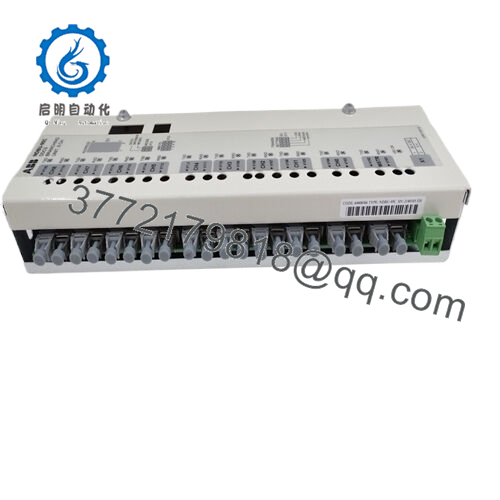
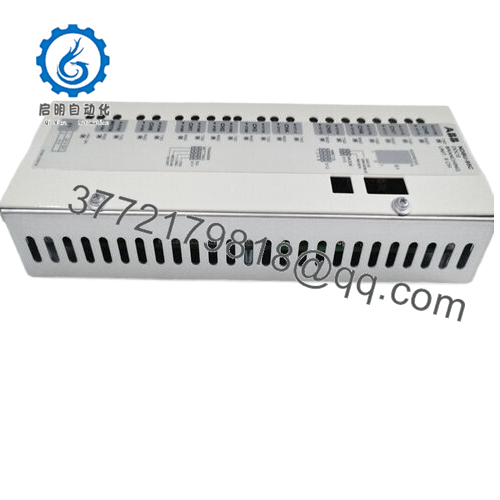
The ABB NDBU-95C functions as a star connection branching unit within ABB’s DDCS framework, essentially acting as an optical splitter that divides a single incoming fiber optic signal into nine independent outputs. This setup is tailored for ABB’s drive systems, including the ACS800 and DCS800 series, where it serves as a key networking component to propagate diagnostic and control data across multiple inverters and motors. In the overall architecture, it mounts passively between the master communication module and slave units, creating a point-to-multipoint topology that simplifies cabling while enhancing signal distribution without active amplification.
Positioned as a reliable extender in fiber optic chains, the ABB NDBU-95C excels in environments needing distributed intelligence, like multi-drive setups in extrusion lines or crane controls. It connects via standard plastic fiber connectors, compatible with ABB’s optical bus standards, and integrates effortlessly into larger 800xA automation platforms for holistic system oversight. For integrators, its plug-and-play nature means less time wrestling with custom wiring— just snap it into a control rack, and it handles the fan-out, supporting baud rates up to 10 Mbps to keep pace with high-speed process demands.
- NDBU-95C 64008366
- NDBU-95C 64008366
Engineers gravitate toward the ABB NDBU-95C for its no-fuss reliability in harsh settings, where it outperforms copper alternatives by resisting EMI from nearby high-voltage lines. With a coated design for added protection, it fits into rack-mounted or panel-integrated configurations, scaling from small skid-mounted pumps to expansive conveyor networks. The value shines in reduced installation complexity; one unit replaces multiple point-to-point links, lowering material costs and commissioning hassles. As industries shift toward IIoT-enabled drives, this branching unit provides a stable backbone, future-proofing investments by accommodating software upgrades for enhanced diagnostics without hardware swaps.
Key Technical Features & Functional Benefits
Signal distribution with the ABB NDBU-95C is all about precision and breadth—taking one input and reliably splitting it across nine channels at 10 Mbps each, which means diagnostics from a central controller hit every connected drive without attenuation or crosstalk. In practice, this translates to faster fault isolation in a paper mill’s winding section, where a jammed roll sensor alert propagates instantly, averting paper tears that could waste thousands of meters. Its passive operation draws zero power, eliminating another potential failure point and ensuring the network stays up even if adjacent electronics falter. Technicians note how this design inherently boosts error tolerance, as optical isolation keeps electrical noise at bay, a boon in weld shops buzzing with arc flashes.
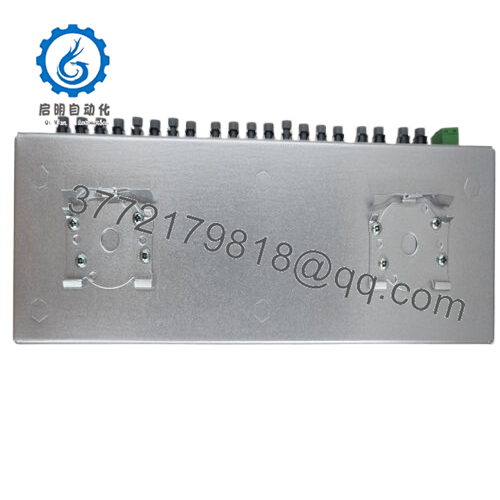
Hardware-wise, the ABB NDBU-95C punches above its weight with a compact, coated enclosure that shrugs off industrial grit. Measuring roughly 102 x 51 x 279 mm and tipping the scales at under 0.7 kg, it slips into tight DIN rail spots or 19-inch racks without dominating space. The plastic fiber compatibility keeps it lightweight yet tough, with connectors rated for repeated cycles in vibrating environments like offshore platforms. Environmental resilience stands out too; it operates steadily from -25°C to +70°C, handling humidity swings that plague uncoated splitters, and its G3 corrosion protection extends usability in chemical-laden atmospheres.
When it comes to compatibility, the ABB NDBU-95C slots into ABB’s ecosystem like a well-oiled gear, pairing with modules like the DDCS master interface for end-to-end fiber chains up to kilometers long. It supports star topologies that branch to PROFIBUS slaves or HART-enabled field devices, easing migrations from legacy systems to modern Ethernet backbones. Longevity is baked in through low insertion loss—typically under 1 dB per channel—which preserves signal strength over distance, minimizing recalibrations. For reliability, the unit’s MTBF exceeds 100,000 hours, backed by no-moving-parts simplicity that sidesteps wear in dusty mills. Integrators praise how it streamlines troubleshooting, with visual status indicators for quick link verification, ultimately slashing lifecycle costs in high-uptime sectors like utilities.
Detailed Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Model | NDBU-95C |
| Brand | ABB |
| Type | Optical Branching Unit |
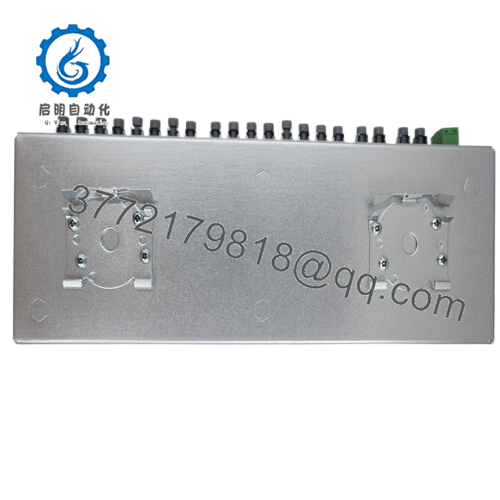
| Channels | 1 input / 9 outputs |
| Data Rate | 10 Mbps per channel |
| Fiber Type | Plastic optical fiber |
| Operating Temperature | -25 to +70 °C |
| Mounting | DIN rail or 19-inch rack |
| Dimensions | 102 x 51 x 279 mm |
| Weight | 0.7 kg |
| Interfaces | Optical fiber connectors (9 outputs) |
| Certifications | CE, RoHS |
| Insertion Loss | <1 dB per channel |
| Environmental Rating | IP20, G3 corrosion protection |
Related Modules or Compatible Units
NDBU-91 – Compact branching unit with fewer channels, suited for smaller DDCS networks where space is at a premium alongside the ABB NDBU-95C.
NDBU-85 – Earlier variant for legacy ACS drives, providing similar optical splitting but with adjusted connectors for phased upgrades.
NDBU-85C – Coated model like the ABB NDBU-95C, optimized for corrosive settings in chemical processing tie-ins.
APBU-44C – Adapter plate for bus unit integration, enabling the ABB NDBU-95C to mount securely in mixed-rack configurations.
DDCS-II Master – Communication interface that feeds signals into the ABB NDBU-95C, forming the core of drive diagnostic chains.
ACS800 Drive Module – Variable frequency drive that receives branched outputs from the ABB NDBU-95C for synchronized motor control.
RDCU-12C – Resolver interface unit, often downstream in networks using the ABB NDBU-95C for position feedback loops.
AINT-01 – Analog input module compatible via DDCS, extending the ABB NDBU-95C‘s reach to sensor aggregation.
Installation Notes & Maintenance Best Practices
Positioning the ABB NDBU-95C starts with assessing fiber run lengths—keep inputs under 100 meters for plastic optics to avoid signal degradation, and route cables away from sharp bends or heat sources like power cables that could warp the fiber. Secure it on a DIN rail with at least 20 mm gaps on sides for access, and ground the mounting frame to dissipate any static buildup, especially in dry milling environments. During hookup, polish connectors lightly if reusing, then test continuity with an optical power meter to confirm even splitting across all nine ports. Align the unit horizontally to prevent dust settling on lenses, and label each output channel clearly for future tracing—overlooked details like this save hours during expansions.
Maintenance on the ABB NDBU-95C boils down to proactive checks rather than reactive fixes. Every quarter, inspect fiber terminations for cracks or dirt using a bright light source; a quick alcohol wipe often restores clarity without full disassembly. Monitor network logs through the connected DDCS master for attenuation spikes, which might signal a failing link, and swap fibers seasonally in high-vibration zones like foundries. No firmware means no updates, but verify compatibility during system audits by simulating a channel drop—expect zero downtime if redundancies are in place. In coastal installs, the coating helps, but annual enclosure checks for pitting keep it compliant. These habits not only prolong its 15-plus-year service life but also integrate smoothly into broader plant reliability programs.





 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626