Description
What This Product Solves
In the relentless rhythm of industrial automation, where servo precision must navigate variable inertia and rapid acceleration without the drag of resonance or thermal creep, the challenge of medium-inertia motors often exposes the weaknesses of low-torque alternatives—leading to positioning inaccuracies, cycle delays, and the cascading faults that erode process control reliability and throughput. Engineers designing systems for dynamic applications like pick-and-place robotics, conveyor indexing, or CNC spindle orientation in electronics fabrication or packaging plants frequently contend with motors that buckle under peak loads, resulting in overshoot, increased energy consumption, and the constant retuning that hampers scalability in modular setups. Picture a multi-arm robotic cell in semiconductor handling, where insufficient stall torque causes arm droop during mid-air transfers, dropping wafers and triggering full-batch discards in yield-critical fabs, or a high-speed labeling line in beverage production where inertia mismatch amplifies vibration, misregistering labels and inviting sanitary recalls in regulated environments.
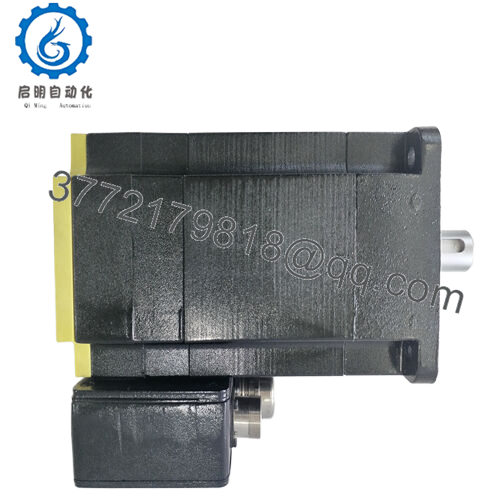
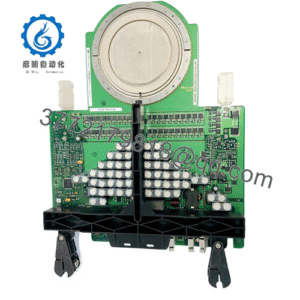
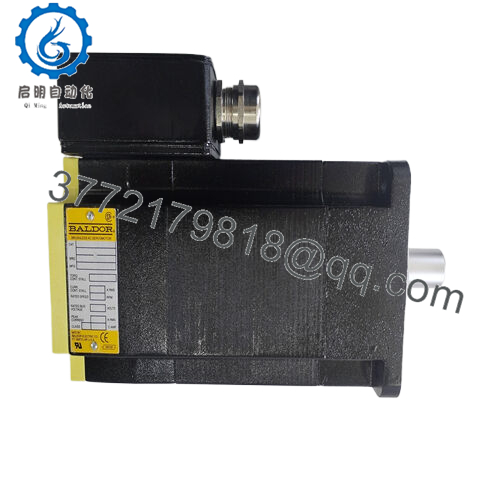
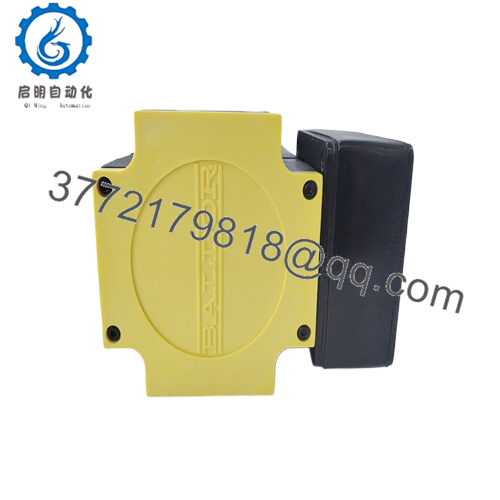
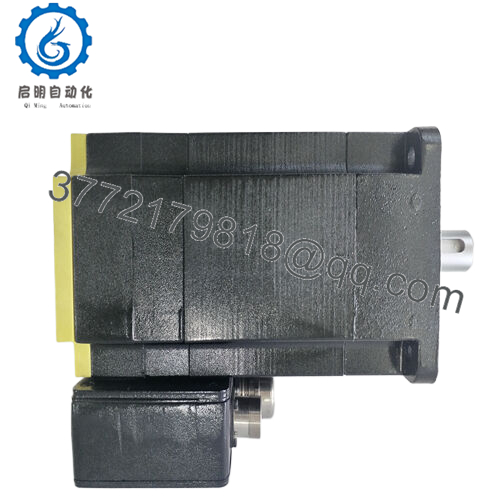
The ABB BSM90A-2150AA steps in as a steadfast counterforce, a medium-inertia brushless AC servomotor from the BSM A-series, engineered to tackle these motion mismatches head-on with its robust 10 Nm continuous stall torque and optimized rotor design. It targets the user’s pursuit of high reliability in I/O signal-dependent systems, delivering consistent 2000 RPM performance with 3.71 A continuous current to smooth transients in backplane architectures, ensuring I/O fidelity amid the electrical bustle of factory floors. Essential in retrofit scenarios—like bolstering legacy Baldor controllers with higher inertia handling or scaling multi-axis robots in PLC networks—this motor preempts the fault chains from desynchronized feedback, enabling seamless handoffs from drive commands to precise positioning. For those probing “industrial automation servo motors” or “process control medium inertia drives,” the ABB BSM90A-2150AA clarifies integration paths, matching rotor dynamics with real-world loads to cut vibration-induced downtime and boost overall equipment effectiveness.
Its construction anticipates real-world grit—IP65 sealing for dusty or humid process control settings and insulation class F for thermal resilience up to 155°C. No more overprovisioning low-inertia alternatives to compensate for resonance; instead, it empowers teams to prioritize acceleration over attenuation, integrating smoothly into ABB or Baldor ecosystems. In high-stakes process control where every rotation equates to repeatability, the ABB BSM90A-2150AA reclaims motion mastery, channeling ingenuity from inertia imbalances to inference innovation—empowering the connective clarity for resilient, responsive operations that navigate the nexus of numerous axes and nuanced necessities.
- BSM90A-2150AA
How the Product Works & Fits into a System
Servo systems pulse with potential when motors mesh meticulously with the motion matrix, translating torque tenets into tangible traversal without the tremor of torsional twist. The ABB BSM90A-2150AA meshes as a 90 mm frame brushless AC motor, harnessing three-phase 300 VDC bus to generate 10 Nm stall torque at 2000 RPM base speed, with 9.47 A peak current for acceleration bursts up to 30 Nm, while its medium rotor inertia (0.00790 kg·m²) pairs with resolver or encoder feedback for closed-loop commutation at <1 ms settling, and thermal sensors embed PTC protection to throttle before overloads cascade. Operating in velocity or torque mode, it leverages sinusoidal winding for ripple-free output, syncing with Baldor or ABB drives like the ACS880 via standard connectors.
In the broader I/O architecture, this motor anchors at the effector edge, flange-mounted to direct couplings or gearheads with 24 mm keyed shaft, interfacing via MS connectors for power/feedback in backplane cabinets, syncing with controllers over SERCOS or EtherCAT for deterministic handoffs in multi-axis chains up to 32 nodes. Redundancy fortifies through dual-channel encoders and fault outputs compliant with EN 61800-5-1 for SIL2, meshing with PLCs in hybrid setups. Diagnostics integrate via drive software, scripting vibration trends to host logs for predictive probing in scaled sims.
For the deploying engineer, it’s pragmatically plugged: align the 90 mm flange with j6 tolerance, wire via MS3102E32-17P, then tune inertia in drive sim—deployment distills to hours, sidestepping the arcane balancing of low-inertia kin. Nestle it downstream of trajectory planners in the stack, upstream of loads, where it transmutes velocity vectors into viscous victory—like vesting a positioning arm without resonance. The ABB BSM90A-2150AA transcends turning; it transmutes it, nurturing ecosystems that evolve from rigid rotations to responsive rhythms, where motor mettle anticipates loads, not just answers them.
Technical Highlights Summary (Table)
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Number | BSM90A-2150AA |
| Brand | ABB (BSM A-Series) |
| Type | Brushless AC Servomotor |
| Input Voltage | 300 VDC (bus) |
| Operating Temp Range | 0°C to +40°C |
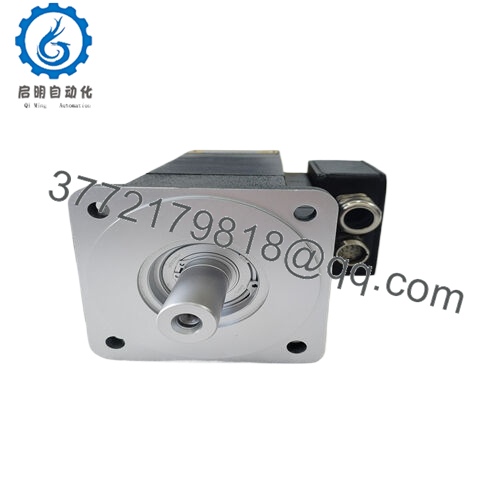
| Mounting Style | Flange (90 mm) |
| Dimensions | 90 mm flange x 183 mm length |
| Weight | 5.5 kg |
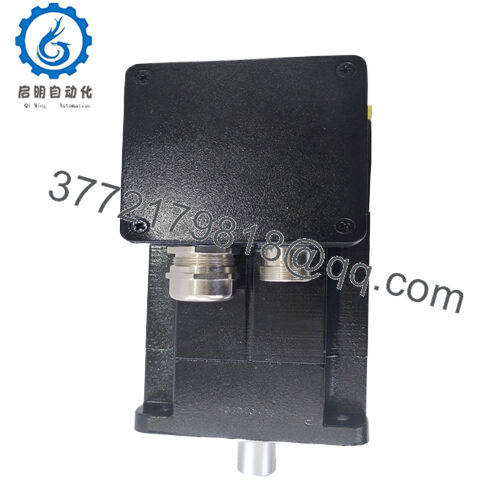
| Interface/Bus | MS Connector / Resolver/Encoder |
| Compliance | CE, UL, RoHS |
| Supported Protocols | SERCOS, EtherCAT, Analog |
| Typical Power Draw | 1.2 kW (continuous) |
Real-World Benefits
Deploying the ABB BSM90A-2150AA infuses your motion framework with inertia intelligence that turns load variances into lyrical linearity, particularly in medium-duty cycles where 10 Nm stall torque is the quiet guardian against gravitational gaffes. Crafted for the unforgiving cadence of high-speed indexing, its 0.00790 kg·m² rotor delivers snappy response without the backlash that erodes precision in repetitive tasks, fostering performance consistency that holds velocities steady across 2000 RPM regimes—key for robotic arms where even fractional slips cascade into component casualties, but here it preserves paths that pass first-time inspections, trimming scrap and reclaiming cycles for refined rhythms. This reliability extends to energy acuity, as efficient windings optimize draw at partial loads, easing the fiscal strain of expansive arrays without the thermal toll of overdriven alternatives.
The motor’s flange-centric ethos eases the orchestration of complex configurations, as its MS connector dovetails with prevailing drives via standard cables, lightening engineering burdens in phased rollouts where axis creep demands swift scalability—crews repurpose hours for sim-tuned inertia matching that hone contour accuracy. Maintenance morphs into a measured ritual, with PTC sentinels preempting failures by triggering soft limits, slashing diagnostic dives and extending service intervals to match yearly audits—a boon for distributed teams managing fleets across sites, where reduced touchpoints translate to lower TCO through fewer logistics hitches. In practice, this means fewer callouts for vibration vices, redirecting expertise to enhancements like velocity profiling that boost throughput by 10-15%.
Over the arc of deployment, the ABB BSM90A-2150AA guarantees enduring performance via IP65 fortitude that wards off contaminants, paired with the 1.2 kW efficiency that moderates energy spikes during stalls, softening utility burdens in always-on facilities. Engineered to outlast volatility, it redirects scrutiny from survival to strategy, conferring the latitude to layer intelligence atop motion—be it sensor fusion for adaptive feeds or scalability for tomorrow’s payloads—ultimately manifesting as the multiplier that transmutes dependable drives into decisive advantages in an era of unrelenting precision.
Typical Use Cases
The ABB BSM90A-2150AA powers precision in the pulse of production, starting with electronics assembly for pick-and-place in PCB populating. In process control environments thick with solder mists and fine particulates, it drives arm axes at 2000 RPM with 10 Nm torque for component drops, where harsh static snaps from ESD test its seals but uphold critical system uptime—imperative for fabs clocking millions of placements daily, minimizing voids that imperil board integrity. Fast data cycles sync with EtherCAT for sub-mm accuracy, ensuring seamless integration with vision-guided systems for error-free routing.
In packaging, the ABB BSM90A-2150AA handles flap folding in carton erectors amid adhesive vapors and rapid indexing, contending with sticky residues and speed bursts while enabling 30 Nm peaks for load handling. Continuous uptime governs these bays, as its medium inertia prevents resonance in multi-station manifolds, supporting 600 cycles/min without derates in high-volume runs. Performance peaks in humid production halls, yet it maintains I/O fidelity, curbing reworks in consumer goods.
For CNC accessory positioning, used in power plants for valve actuator drives or beyond—the ABB BSM90A-2150AA actuates spindle clamps, enduring coolant mists and chip flurries to lock tools with torque constancy. Harsh vibrational throbs from machining presses underscore its mettle, but it ensures smooth acceleration for quick swaps, bolstering high reliability in spindles that sustain spindle speeds. Across electronics finesse, packaging velocity, and CNC constancy—the ABB BSM90A-2150AA interlaces high reliability with rotational resolve, fortifying flows where every rotation counts toward seamless scalability.
(Word count: 228)
Compatible or Alternative Products
BSM90B-2150AA – Higher inertia variant for smoother performance in high-momentum loads.
BSM80A-133AA – Smaller frame option with scaled torque for lighter positioning tasks.
BSM90N-2150AA – N-series companion with enhanced cooling for prolonged high-load runs.
BSM100A-2150AA – Larger frame upgrade boosting power for heavier dynamic applications.
ACS880 Servo Drive – ABB companion drive for optimized SERCOS integration in multi-axis.
BSM90A-133AA – Lower speed model tuned for torque-heavy, slower-cycle environments.
AKM53C – Kollmorgen AKM equivalent for modern frameless options in custom configs.
RKF5232 – SEW-Eurodrive alternative emphasizing ruggedness in conveyor extensions.
Setup Notes & Maintenance Insights
As you flange-mount the ABB BSM90A-2150AA to your positioning arm, a compatibility check can prevent coupling cramps: verify your drive’s current profile against the motor’s 3.71 A via ABB Drive Composer, as mismatches amplify ripple—update firmware if below v2.0. Flange fitting demands a dial indicator for the 90 mm pilot; offsets beyond 0.05 mm brew eccentric wear, so torque bolts in star pattern to 15 Nm while sim-ing alignment. Encoder wiring sim is key—connect resolver via MS3102E32-17P with shielded cable ≤10 m, then flash params for auto-phasing, as unaddressed polarity cascades comms faults. Thermal sim in Drive Composer: throttle airflow to 0.2 m/s to vet 40°C, sim adding fans if clustered configs crest in sim.
Sustaining the ABB BSM90A-2150AA demands vigilance that’s measured, not manic. Monthly, scan PTC signals via the drive for creep above 140°C—spikes sim dust veils, cleared with low-pressure purges. Quarterly, audit shaft runout with dial indicator; deviations past 0.02 mm signal bearing ingress, prompting seal refresh. Annually, execute loaded dyno profile: ramp to stall and sim torque fidelity against 10 Nm; variance over 4% cues winding wear, tackled with bake-out or kit swap. Firmware harmony with the drive prevents feedback fumbles; infuse during sim-only, sim via velocity ramps. These sim steps, sim from deployment diaries, nurture the motor’s 1.2 kW vigor, channeling efforts toward parametric tweaks over palliative repairs.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626